Assessment of Quantitative and Allelic MGMT Methylation Patterns as a Prognostic Marker in Glioblastoma
- PMID: 26883115
- PMCID: PMC4777218
- DOI: 10.1093/jnen/nlv024
Assessment of Quantitative and Allelic MGMT Methylation Patterns as a Prognostic Marker in Glioblastoma
Abstract
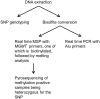
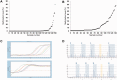
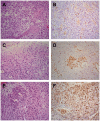
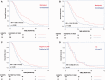
Methylation of the O(6)-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) gene is a predictive and prognostic marker in newly diagnosed glioblastoma patients treated with temozolomide but how MGMT methylation should be assessed to ensure optimal detection accuracy is debated. We developed a novel quantitative methylation-specific PCR (qMSP) MGMT assay capable of providing allelic methylation data and analyzed 151 glioblastomas from patients receiving standard of care treatment (Stupp protocol). The samples were also analyzed by immunohistochemistry (IHC), standard bisulfite pyrosequencing, and genotyped for the rs1690252 MGMT promoter single nucleotide polymorphism. Monoallelic methylation was observed more frequently than biallelic methylation, and some cases with monoallelic methylation expressed the MGMT protein whereas others did not. The presence of MGMT methylation was associated with better overall survival (p = 0.006; qMSP and p = 0.002; standard pyrosequencing), and the presence of the protein was associated with worse overall survival (p = 0.009). Combined analyses of qMSP and standard pyrosequencing or IHC identified additional patients who benefited from temozolomide treatment. Finally, low methylation levels were also associated with better overall survival (p = 0.061; qMSP and p = 0.02; standard pyrosequencing). These data support the use of both MGMT methylation and MGMT IHC but not allelic methylation data as prognostic markers in patients with temozolomide-treated glioblastoma.
Keywords: Alkylating agents; Allele-specific; Glioblastoma; Immunohistochemistry; MGMT; Methylation; Temozolomide..
© 2016 American Association of Neuropathologists, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Esteller M, Garcia-Foncillas J, Andion E, et al. Inactivation of the DNA-repair gene MGMT and the clinical response of gliomas to alkylating agents. N Engl J Med 2000;343:1350–4 - PubMed
-
- Hegi ME, Diserens AC, Gorlia T, et al. MGMT gene silencing and benefit from temozolomide in glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 2005;352:997–1003 - PubMed
-
- Hegi ME, Diserens AC, Godard S, et al. Clinical trial substantiates the predictive value of O-6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase promoter methylation in glioblastoma patients treated with temozolomide. Clin Cancer Res 2004;10:1871–4 - PubMed
-
- Wick W, Weller M, van den Bent M, et al. MGMT testing–the challenges for biomarker-based glioma treatment. Nat Rev Neurol 2014;10:372–85 - PubMed
-
- Wick W, Platten M, Meisner C, et al. Temozolomide chemotherapy alone versus radiotherapy alone for malignant astrocytoma in the elderly: The NOA-08 randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 2012;13:707–15 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

