Effectiveness of two different doses of rituximab for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in an international cohort: data from the CERERRA collaboration
- PMID: 26883119
- PMCID: PMC4756505
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-016-0951-z
Effectiveness of two different doses of rituximab for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in an international cohort: data from the CERERRA collaboration
Erratum in
-
Erratum to: Effectiveness of two different doses of rituximab for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in an international cohort: data from the CERERRA collaboration.Arthritis Res Ther. 2016 Jun 20;18(1):144. doi: 10.1186/s13075-016-1048-4. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 27324256 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: The approved dose of rituximab (RTX) in rheumatoid arthritis is 1000 mg × 2, but some data have suggested similar clinical efficacy with 500 mg × 2. The purpose of this study was to compare the effectiveness of the regular and low doses given as first treatment course.
Methods: Twelve European registries participating in the CERERRA collaboration (The European Collaborative Registries for the Evaluation of Rituximab in Rheumatoid Arthritis) submitted anonymized datasets with demographic, efficacy and treatment data for patients who had started RTX. Treatment effectiveness was assessed by DAS28 reductions and EULAR responses after 6 months.
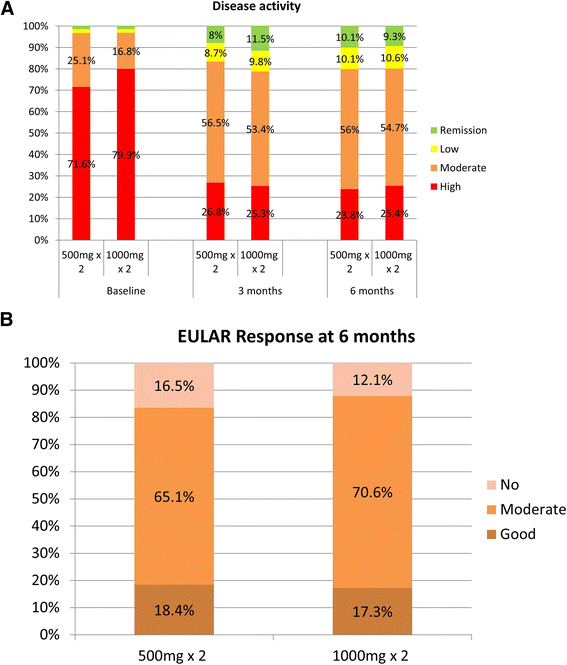
Results: Data on RTX dose were available for 2,873 patients, of whom 2,625 (91.4 %) and 248 (8.6 %) received 1000 mg × 2 and 500 mg × 2, respectively. Patients treated with 500 mg × 2 were significantly older, had longer disease duration, higher number of prior DMARDs, but lower number of prior biologics and lower baseline DAS28 than those treated with 1000 mg × 2. Fewer patients in the low-dose group received concomitant DMARDs but more frequently received concomitant corticosteroids. Both doses led to significant clinical improvements at 6 months. DAS28 reductions at 6 months were comparable in the 2 dose regimens [mean DeltaDAS28 ± SD -2.0 ± 1.3 (high dose) vs. -1.7 ± 1.4 (low dose), p = 0.23 adjusted for baseline differences]. Similar percentages of patients achieved EULAR good response in the two dose groups, 18.4 % vs. 17.3 %, respectively (p = 0.36).
Conclusions: In this large observational cohort initial treatment with RTX at 500 mg × 2 and 1000 mg × 2 led to comparable clinical outcomes at 6 months.
Figures
References
-
- Cohen SB, Emery P, Greenwald MW, Dougados M, Furie RA, Genovese MC, et al. Rituximab for rheumatoid arthritis refractory to anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy: Results of a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III trial evaluating primary efficacy and safety at twenty-four weeks. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:2793–806. doi: 10.1002/art.22025. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chatzidionysiou K, Lie E, Nasonov E, Lukina G, Hetland ML, Tarp U, et al. Highest clinical effectiveness of rituximab in autoantibody-positive patients with rheumatoid arthritis and in those for whom no more than one previous TNF antagonist has failed: pooled data from 10 European registries. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70:1575–80. doi: 10.1136/ard.2010.148759. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Emery P, Deodhar A, Rigby WF, Isaacs JD, Combe B, Racewicz AJ, et al. Efficacy and safety of different doses and retreatment of rituximab: a randomised, placebo-controlled trial in patients who are biological naive with active rheumatoid arthritis and an inadequate response to methotrexate (Study Evaluating Rituximab’s Efficacy in MTX iNadequate rEsponders (SERENE)) Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69:1629–35. doi: 10.1136/ard.2009.119933. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

