Cost Effectiveness of Paliperidone Long-Acting Injectable Versus Other Antipsychotics for the Maintenance Treatment of Schizophrenia in France
- PMID: 26883132
- PMCID: PMC4796324
- DOI: 10.1007/s40273-015-0348-x
Cost Effectiveness of Paliperidone Long-Acting Injectable Versus Other Antipsychotics for the Maintenance Treatment of Schizophrenia in France
Abstract
Background: French clinical recommendations suggest prescribing long-acting injectable (LAI) antipsychotics to patients with a maintenance treatment indication in schizophrenia. Despite this, and due to their relatively high acquisition and administration costs, LAIs are still underused in clinical practice in France, thus highlighting the need for pharmacoeconomic evaluations.
Objective: Our objective was to estimate the cost effectiveness of paliperidone LAI (or paliperidone palmitate), a once-monthly second-generation LAI antipsychotic, compared with the most common antipsychotic medications for the maintenance treatment of schizophrenia in France.
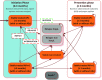
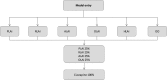
Methods: A Markov model was developed to simulate the progression of a cohort of schizophrenic patients through four health states (stable treated, stable non-treated, relapse and death) and to consider up to three lines of treatment to account for changes in treatment management. Paliperidone LAI was compared with risperidone LAI, aripiprazole LAI, olanzapine LAI, haloperidol LAI (or haloperidol decanoate) and oral olanzapine. Costs, quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs) and number of relapses were assessed over 5 years based on 3-month cycles with a discount rate of 4% and from a French health insurance perspective. Patients were considered to be stabilised after a schizophrenic episode and would enter the model at an initiation phase, followed by a prevention of relapse phase if successful. Data (e.g. relapse or discontinuation rates) for the initiation phase came from randomised clinical trials, whereas relapse rates in the prevention phase were derived from hospitalisation risks based on real-life French data to capture adherence effects. Safety and utility data were derived from international publications. Additionally, costs were retrieved from French health insurance databases and publications. Finally, expert opinion was used for validation purposes or in case of gaps in data. The robustness of results was assessed through deterministic and probabilistic sensitivity analyses.
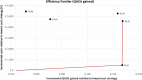
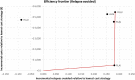
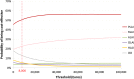
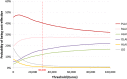
Results: All LAI antipsychotics were found to have similar costs over 5 years: approximatively €55,000, except for paliperidone LAI which had a discounted cost of €50,880. Oral olanzapine was less costly than LAIs (i.e. €50,379 after 5 years) but was associated with fewer QALYs gained and relapses avoided. Paliperidone LAI dominated aripiprazole LAI, olanzapine LAI and haloperidol LAI in terms of costs per QALY, and it was associated with slightly fewer QALYs when compared with risperidone LAI (i.e. 3.763 vs 3.764). This resulted in a high incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) (i.e. €4,770,018 per QALY gained) for risperidone LAI compared with paliperidone LAI. Paliperidone LAI was more costly than olanzapine oral but associated with more QALYs (i.e. ICER of €2411 per QALY gained for paliperidone LAI compared with oral olanzapine). Paliperidone LAI had a probability of being the optimal strategy in more than 50% of cases for a willingness-to-pay threshold of €8000 per QALY gained.
Conclusion: This analysis, to the best of our knowledge, is the first of its kind to assess the cost effectiveness of antipsychotics based on French observational data. Paliperidone LAI appeared to be a cost-effective option in the treatment of schizophrenia from the French health insurance perspective.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Comparison of medical and economic benefits of antipsychotics in the treatment of schizophrenia in France].Encephale. 2017 Aug;43(4):311-320. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2016.02.021. Epub 2016 Sep 9. Encephale. 2017. PMID: 27623123 French.
-
Cost-effectiveness Analysis of Aripiprazole Once-Monthly for the Treatment of Schizophrenia in the UK.J Ment Health Policy Econ. 2015 Dec;18(4):185-200. J Ment Health Policy Econ. 2015. PMID: 26729007
-
Economic analysis of paliperidone long-acting injectable for chronic schizophrenia in Portugal.J Med Econ. 2016 Sep;19(9):913-21. doi: 10.1080/13696998.2016.1184156. Epub 2016 May 13. J Med Econ. 2016. PMID: 27124697
-
[Cost-effectiveness analysis of schizophrenic patient care settings: impact of an atypical antipsychotic under long-acting injection formulation].Encephale. 2005 Mar-Apr;31(2):235-46. doi: 10.1016/s0013-7006(05)82390-5. Encephale. 2005. PMID: 15959450 Review. French.
-
Cost-effectiveness of olanzapine long-acting injection in the treatment of patients with schizophrenia in the United States: a micro-simulation economic decision model.Curr Med Res Opin. 2011 Apr;27(4):713-30. doi: 10.1185/03007995.2011.554533. Epub 2011 Jan 25. Curr Med Res Opin. 2011. PMID: 21265593 Review.
Cited by
-
The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the trend of prescribing long-acting injections of paliperidone and risperidone in Central Serbia.Front Psychiatry. 2023 Dec 21;14:1301835. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1301835. eCollection 2023. Front Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 38179245 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review of the methods of health economic models assessing antipsychotic medication for schizophrenia.PLoS One. 2020 Jul 10;15(7):e0234996. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0234996. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32649663 Free PMC article.
-
Mental healthcare utilisation by patients before and after receiving paliperidone palmitate treatment: mirror image analyses.BMJ Open. 2022 Apr 6;12(4):e051567. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-051567. BMJ Open. 2022. PMID: 35387806 Free PMC article.
-
Invega Hafyera (Paliperidone Palmitate): Extended-Release Injectable Suspension for Patients With Schizophrenia.J Pharm Technol. 2023 Apr;39(2):88-94. doi: 10.1177/87551225231153541. Epub 2023 Mar 16. J Pharm Technol. 2023. PMID: 37051282 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systematic review of pharmacoeconomic models for schizophrenia.J Mark Access Health Policy. 2018 Aug 14;6(1):1508272. doi: 10.1080/20016689.2018.1508272. eCollection 2018. J Mark Access Health Policy. 2018. PMID: 30128087 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organisation (WHO). Schizophrenia: Fact sheet N°397 [database on the Internet] 2014 [cited 04/11/2014]. Available from: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs397/en/.
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). Schizophrenia and public health. 1996.
-
- Haute Autorité de Santé (HAS). Commission de la Transparence—Avis du 1er février 2012 : XEPLION. 2012.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

