Recent progress in chromogenic and fluorogenic chemosensors for hypochlorous acid
- PMID: 26883493
- PMCID: PMC4789306
- DOI: 10.1039/c6an00158k
Recent progress in chromogenic and fluorogenic chemosensors for hypochlorous acid
Abstract
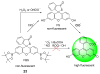
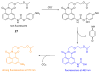
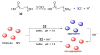
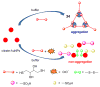
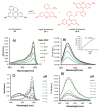
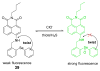
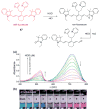
Due to the biological and industrial importance of hypochlorous acid, the development of optical probes for HOCl has been an active research area. Hypochlorous acid and hypochlorite can oxidize electron-rich analytes with accompanying changes in molecular sensor spectroscopic profiles. Probes for such processes may monitor HOCl levels in the environment or in an organism and via bio-labeling or bioimaging techniques. This review summarizes recent developments in the area of chromogenic and fluorogenic chemosensors for HOCl.
Figures



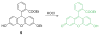

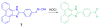
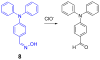



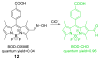

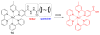
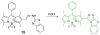


















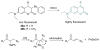


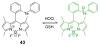
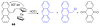







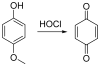



Similar articles
-
Fluorescence turn-on detection of hypochlorous acid via HOCl-promoted dihydrofluorescein-ether oxidation and its application in vivo.Chem Commun (Camb). 2012 May 16;48(39):4677-9. doi: 10.1039/c2cc30265a. Epub 2012 Mar 2. Chem Commun (Camb). 2012. PMID: 22389025
-
A highly selective turn-on fluorescent probe for hypochlorous acid based on hypochlorous acid-induced oxidative intramolecular cyclization of boron dipyrromethene-hydrazone.Anal Chim Acta. 2015 Jul 2;882:68-75. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2015.04.012. Epub 2015 Apr 9. Anal Chim Acta. 2015. PMID: 26043093
-
A cyanine-based near-infrared fluorescent probe for highly sensitive and selective detection of hypochlorous acid and bioimaging.Talanta. 2016 Dec 1;161:592-598. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2016.09.008. Epub 2016 Sep 5. Talanta. 2016. PMID: 27769452
-
Imaging of Hypochlorous Acid by Fluorescence and Applications in Biological Systems.Chem Asian J. 2019 Sep 16;14(18):3048-3084. doi: 10.1002/asia.201900672. Epub 2019 Sep 2. Chem Asian J. 2019. PMID: 31347256 Review.
-
Recent development of synthetic probes for detection of hypochlorous acid/hypochlorite.Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2020 Oct 15;240:118545. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2020.118545. Epub 2020 May 31. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2020. PMID: 32521447 Review.
Cited by
-
A novel highly specific and ultrasensitive fluorescent probe for monitoring hypochlorous acid and its application in live cells.RSC Adv. 2019 Feb 6;9(8):4659-4664. doi: 10.1039/c8ra09551e. eCollection 2019 Jan 30. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35520202 Free PMC article.
-
Quinoline-based fluorescent probe for the detection and monitoring of hypochlorous acid in a rheumatoid arthritis model.RSC Adv. 2021 Sep 24;11(50):31656-31662. doi: 10.1039/d1ra06224g. eCollection 2021 Sep 21. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35496887 Free PMC article.
-
A New and Fast-Response Fluorescent Probe for Monitoring Hypochlorous Acid Derived from Myeloperoxidase.Molecules. 2023 Aug 14;28(16):6055. doi: 10.3390/molecules28166055. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37630307 Free PMC article.
-
Malononitrile as the 'double-edged sword' of passivation-activation regulating two ICT to highly sensitive and accurate ratiometric fluorescent detection for hypochlorous acid in biological system.Sens Actuators B Chem. 2020 Dec 15;325:128793. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2020.128793. Epub 2020 Aug 25. Sens Actuators B Chem. 2020. PMID: 32863585 Free PMC article.
-
A pyrene-based ratiometric fluorescent probe with a large Stokes shift for selective detection of hydrogen peroxide in living cells.J Pharm Anal. 2020 Oct;10(5):490-497. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2020.07.003. Epub 2020 Aug 4. J Pharm Anal. 2020. PMID: 33133733 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vijayaraghavan K, Ramanujam TK, Balasubramanian N. Waste Manage. 1999;19:319–323.
-
- Sun MT, Yu H, Zhu HJ, Ma F, Zhang S, Huang DJ, Wang SH. Anal Chem. 2014;86:671–677. - PubMed
-
- Ye ZQ, Zhang R, Song B, Dai ZC, Jin DY, Goldys EM, Yuan JL. Dalton Trans. 2014;43:8414–8420. - PubMed
-
- Koide Y, Urano Y, Hanaoka K, Terai T, Nagano T. J Am Chem Soc. 2011;133:5680–5682. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

