N-Terminal Acetylation-Targeted N-End Rule Proteolytic System: The Ac/N-End Rule Pathway
- PMID: 26883906
- PMCID: PMC4794598
- DOI: 10.14348/molcells.2016.2329
N-Terminal Acetylation-Targeted N-End Rule Proteolytic System: The Ac/N-End Rule Pathway
Abstract
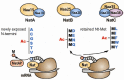
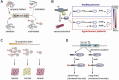
Although Nα-terminal acetylation (Nt-acetylation) is a pervasive protein modification in eukaryotes, its general functions in a majority of proteins are poorly understood. In 2010, it was discovered that Nt-acetylation creates a specific protein degradation signal that is targeted by a new class of the N-end rule proteolytic system, called the Ac/N-end rule pathway. Here, we review recent advances in our understanding of the mechanism and biological functions of the Ac/N-end rule pathway, and its crosstalk with the Arg/N-end rule pathway (the classical N-end rule pathway).
Keywords: N-end rule; N-terminal acetylation; degron; proteolysis; ubiquitin.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The N-end rule pathway and regulation by proteolysis.Protein Sci. 2011 Aug;20(8):1298-345. doi: 10.1002/pro.666. Protein Sci. 2011. PMID: 21633985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Progress on the role of N-end rule pathways in protein degradation].Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2024 Dec 25;76(6):987-1000. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2024. PMID: 39780575 Review. Chinese.
-
Control of protein degradation by N-terminal acetylation and the N-end rule pathway.Exp Mol Med. 2018 Jul 27;50(7):1-8. doi: 10.1038/s12276-018-0097-y. Exp Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 30054456 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Control of mammalian G protein signaling by N-terminal acetylation and the N-end rule pathway.Science. 2015 Mar 13;347(6227):1249-1252. doi: 10.1126/science.aaa3844. Science. 2015. PMID: 25766235 Free PMC article.
-
The N-end rule pathway enzyme Naa10 supports epiblast specification in mouse embryonic stem cells by modulating FGF/MAPK.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2019 May;55(5):355-367. doi: 10.1007/s11626-019-00341-8. Epub 2019 Apr 16. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2019. PMID: 30993557
Cited by
-
NatB regulates Rb mutant cell death and tumor growth by modulating EGFR/MAPK signaling through the N-end rule pathways.PLoS Genet. 2020 Jun 19;16(6):e1008863. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008863. eCollection 2020 Jun. PLoS Genet. 2020. PMID: 32559195 Free PMC article.
-
NatB Catalytic Subunit Depletion Disrupts DNA Replication Initiation Leading to Senescence in MEFs.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 13;24(10):8724. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108724. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37240070 Free PMC article.
-
NAA10 as a New Prognostic Marker for Cancer Progression.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 28;21(21):8010. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218010. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33126484 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tying up loose ends: the N-degron and C-degron pathways of protein degradation.Biochem Soc Trans. 2020 Aug 28;48(4):1557-1567. doi: 10.1042/BST20191094. Biochem Soc Trans. 2020. PMID: 32627813 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analyzing N-terminal Arginylation through the Use of Peptide Arrays and Degradation Assays.J Biol Chem. 2016 Sep 30;291(40):20976-20992. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.747956. Epub 2016 Aug 10. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27510035 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aksnes H., Drazic A., Arnesen T. (Hyper)tension release by N-terminal acetylation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2015a;40:422–424. - PubMed
-
- Aksnes H., Hole K., Arnesen T. Molecular, cellular, and physiological significance of N-terminal acetylation. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2015b;316:267–305. - PubMed
-
- Aksnes H., Van Damme P., Goris M., Starheim K.K., Marie M., Stove S.I., Hoel C., Kalvik T.V., Hole K., Glomnes N., et al. An organellar nalpha-acetyltransferase, naa60, acetylates cytosolic N termini of transmembrane proteins and maintains Golgi integrity. Cell Rep. 2015c;10:1362–1374. - PubMed
-
- Arnesen T., Van Damme P., Polevoda B., Helsens K., Evjenth R., Colaert N., Varhaug J.E., Vandekerckhove J., Lillehaug J.R., Sherman F., et al. Proteomics analyses reveal the evolutionary conservation and divergence of N-terminal acetyltransferases from yeast and humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2009;106:8157–8162. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arnesen T., Starheim K.K., Van Damme P., Evjenth R., Dinh H., Betts M.J., Ryningen A., Vandekerckhove J., Gevaert K., Anderson D. The chaperone-like protein HYPK acts together with NatA in cotranslational N-terminal acetylation and prevention of Huntingtin aggregation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2010;30:1898–1909. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

