Histone Deacetylase-3/CAGE Axis Targets EGFR Signaling and Regulates the Response to Anti-Cancer Drugs
- PMID: 26883907
- PMCID: PMC4794605
- DOI: 10.14348/molcells.2016.2244
Histone Deacetylase-3/CAGE Axis Targets EGFR Signaling and Regulates the Response to Anti-Cancer Drugs
Abstract
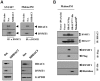
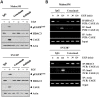
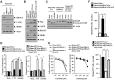
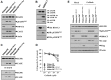
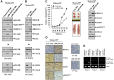
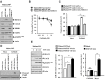
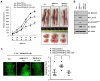
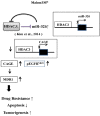
We have previously reported the role of miR-326-HDAC3 loop in anti-cancer drug-resistance. CAGE, a cancer/testis antigen, regulates the response to anti-cancer drug-resistance by forming a negative feedback loop with miR-200b. Studies investigating the relationship between CAGE and HDAC3 revealed that HDAC3 negatively regulated the expression of CAGE. ChIP assays demonstrated the binding of HDAC3 to the promoter sequences of CAGE. However, CAGE did not affect the expression of HDAC3. We also found that EGFR signaling regulated the expressions of HDAC3 and CAGE. Anti-cancer drug-resistant cancer cell lines show an increased expression of pEGFR(Y845). HDAC3 was found to negatively regulate the expression of pEGFR(Y845). CAGE showed an interaction and co-localization with EGFR. It was seen that miR-326, a negative regulator of HDAC3, regulated the expression of CAGE, pEGFR(Y845), and the interaction between CAGE and EGFR. miR-326 inhibitor induced the binding of HDAC3 to the promoter sequences in anti-cancer drug-resistant Malme3M(R) cells, decreasing the tumorigenic potential of Malme3M(R) cells in a manner associated with its effect on the expression of HDAC3, CAGE and pEGFR(Y845). The down-regulation of HDAC3 enhanced the tumorigenic, angiogenic and invasion potential of the anti-cancer drug-sensitive Malme3M cells in CAGE-dependent manner. Studies revealed that PKCδ was responsible for the increased expression of pEGFR(Y845) and CAGE in Malme3M(R) cells. CAGE showed an interaction with PKCδ in Malme3M(R) cells. Our results show that HDAC3-CAGE axis can be employed as a target for overcoming resistance to EGFR inhibitors.
Keywords: CAGE; EGFR; HDAC3; anti-cancer drug-resistance.
Figures


Similar articles
-
miR-217 and CAGE form feedback loop and regulates the response to anti-cancer drugs through EGFR and HER2.Oncotarget. 2016 Mar 1;7(9):10297-321. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7185. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26863629 Free PMC article.
-
miR-326-histone deacetylase-3 feedback loop regulates the invasion and tumorigenic and angiogenic response to anti-cancer drugs.J Biol Chem. 2014 Oct 3;289(40):28019-39. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.578229. Epub 2014 Aug 19. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25138213 Free PMC article.
-
miR-200b and cancer/testis antigen CAGE form a feedback loop to regulate the invasion and tumorigenic and angiogenic responses of a cancer cell line to microtubule-targeting drugs.J Biol Chem. 2013 Dec 20;288(51):36502-18. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.502047. Epub 2013 Oct 30. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24174534 Free PMC article.
-
Role of HDAC3-miRNA-CAGE Network in Anti-Cancer Drug-Resistance.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Dec 23;20(1):51. doi: 10.3390/ijms20010051. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30583572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-30a Regulates the Expression of CAGE and p53 and Regulates the Response to Anti-Cancer Drugs.Mol Cells. 2016 Apr 30;39(4):299-309. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2016.2242. Epub 2016 Feb 25. Mol Cells. 2016. PMID: 26912082 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Targeting Autophagy for Overcoming Resistance to Anti-EGFR Treatments.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Sep 16;11(9):1374. doi: 10.3390/cancers11091374. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31527477 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CAGE Binds to Beclin1, Regulates Autophagic Flux and CAGE-Derived Peptide Confers Sensitivity to Anti-cancer Drugs in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Cells.Front Oncol. 2018 Dec 10;8:599. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2018.00599. eCollection 2018. Front Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30619741 Free PMC article.
-
The combination of a seven-autoantibody panel with computed tomography scanning can enhance the diagnostic efficiency of non-small cell lung cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 30;12:1047019. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1047019. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36531072 Free PMC article.
-
CAGE-miR-140-5p-Wnt1 Axis Regulates Autophagic Flux, Tumorigenic Potential of Mouse Colon Cancer Cells and Cellular Interactions Mediated by Exosomes.Front Oncol. 2019 Nov 14;9:1240. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01240. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31799196 Free PMC article.
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitors suppress aggressiveness of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma via histone acetylation-independent blockade of the EGFR-Arf1 axis.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Feb 18;38(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1080-8. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30777099 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barter M.J., Pybus L., Litherland G.J., Rowan A.D., Clark I.M., Edwards D.R., Cawston T.E., Young D.A. HDAC-mediated control of ERK- and PI3K-dependent TGF-β-induced extracellular matrix-regulating genes. Matrix Biol. 2010;29:602–612. - PubMed
-
- Brodie S.A., Li G., El-Kommos A., Kang H., Ramalingam S.S., Behera M., Gandhi K., Kowalski J., Sica G.L., Khuri F.R., Vertino P.M., Brandes J.C. Class I HDACs are mediators of smoke carcinogen-induced stabilization of DNMT1 and serve as promising targets for chemoprevention of lung cancer. Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila). 2014;7:351–361. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

