Glial Tau Pathology in Tauopathies: Functional Consequences
- PMID: 26884683
- PMCID: PMC4750898
- DOI: 10.4137/JEN.S25515
Glial Tau Pathology in Tauopathies: Functional Consequences
Abstract
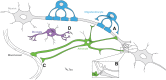
Tauopathies are a class of neurodegenerative diseases characterized by the presence of hyperphosphorylated and aggregated tau pathology in neuronal and glial cells. Though the ratio of neuronal and glial tau aggregates varies across diseases, glial tau aggregates can populate the same degenerating brain regions as neuronal tau aggregates. While much is known about the deleterious consequences of tau pathology in neurons, the relative contribution of glial tau pathology to these diseases is less clear. Recent studies using a number of model systems implicate glial tau pathology in contributing to tauopathy pathogenesis. This review aims to highlight the functional consequences of tau overexpression in glial cells and explore the potential contribution of glial tau pathology in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative tauopathies.
Keywords: astrocytes; functional consequences; glial tau pathology; microglia; neurodegeneration; oligodendrocytes; tau; tauopathy.
Figures
References
-
- Ballatore C, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ. Tau-mediated neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease and related disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007;8(9):663–672. - PubMed
-
- Chin SS, Goldman JE. Glial inclusions in CNS degenerative diseases. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1996;55(5):499–508. - PubMed
-
- Feany MB, Dickson DW. Neurodegenerative disorders with extensive tau pathology: a comparative study and review. Ann Neurol. 1996;40(2):139–148. - PubMed
-
- Williams DR. Tauopathies: classification and clinical update on neurodegenerative diseases associated with microtubule-associated protein tau. Intern Med J. 2006;36(10):652–660. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

