Efficacy of hepatic resection for huge (≥ 10 cm) hepatocellular carcinoma: good prognosis associated with the uninodular subtype
- PMID: 26884976
- PMCID: PMC4723821
Efficacy of hepatic resection for huge (≥ 10 cm) hepatocellular carcinoma: good prognosis associated with the uninodular subtype
Abstract
Background: The value of hepatic resection (HR) for huge hepatocellular carcinomas (HCC) (≥ 10 cm in diameter) remains controversial. The aim of this study is to evaluate the efficacy of hepatic resection (HR) for patients with huge HCC.
Methods: A total of 739 patients with huge HCC (≥ 10 cm in diameter) (huge HCC group, n = 244) or small HCC (< 10 cm in diameter) (small HCC group, n = 495) who received initial HR were retrospectively analyzed. Overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) were obtained using the Kaplan-Meier method and compared by Log-Rank test. Prognostic factors of huge HCC were identified based on Cox regression analyses.
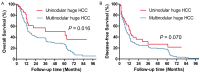
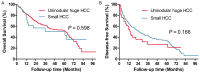
Results: The hospital mortality of these two groups were similar (P = 0.252). The 5-year OS of huge HCC group and small HCC group were 30.3% and 51.9%, respectively (P < 0.001). Uninodular huge HCC had a significant higher 5-year OS (50.6%) than mutinodular huge HCC (26.9%) (P = 0.016). Multivariate analysis revealed that uninodular huge HCC and absence of PVTT independently predicted better OS for huge HCC patients.
Conclusion: HR is a safe and effective approach for the treatment of huge HCC, especially for the uninodular subtype.
Keywords: Hepatic resection; disease-free survival; hepatocellular carcinoma; huge; mortality; overall survival; uninodular.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Long-term outcomes after hepatectomy of huge hepatocellular carcinoma: A single-center experience in China.Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2019 Dec;18(6):532-537. doi: 10.1016/j.hbpd.2019.09.001. Epub 2019 Sep 11. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2019. PMID: 31543313
-
Is hepatectomy for huge hepatocellular carcinoma (≥ 10 cm in diameter) safe and effective? A single-center experience.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15(17):7069-77. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2014.15.17.7069. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014. PMID: 25227793
-
Long-term survival of patients undergoing liver resection for very large hepatocellular carcinomas.Br J Surg. 2016 Oct;103(11):1513-20. doi: 10.1002/bjs.10196. Epub 2016 Aug 23. Br J Surg. 2016. PMID: 27550624
-
Efficacy of hepatic resection vs transarterial chemoembolization for solitary huge hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Aug 28;21(32):9630-7. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i32.9630. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26327771 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic factors of hepatic resection for hepatocellular carcinoma with cirrhosis: univariate and multivariate analysis.J Surg Oncol. 2002 Dec;81(4):195-202. doi: 10.1002/jso.10178. J Surg Oncol. 2002. PMID: 12451624 Review.
Cited by
-
Pre- and Postoperative Models for Prediction of Recurrence in Non-B, Non-C Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2021 Feb 18;11:612588. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.612588. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33680963 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Factors and Survival Outcomes of Surgical Resection of Huge Hepatocellular Carcinomas.J Gastrointest Cancer. 2020 Mar;51(1):250-253. doi: 10.1007/s12029-019-00240-x. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31054105
-
Cirrhotic and non-cirrhotic huge hepatocellular carcinoma (≥ 10 cm): a comparative study of surgical management and follow-up treatment in a single institution.Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2023 Jan 10;408(1):18. doi: 10.1007/s00423-023-02762-2. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2023. PMID: 36627380
-
Does size matter for resection of giant versus non-giant hepatocellular carcinoma? A meta-analysis.World J Gastrointest Surg. 2023 Feb 27;15(2):273-286. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v15.i2.273. World J Gastrointest Surg. 2023. PMID: 36896301 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Nomograms Stratify Survival of Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Without Portal Vein Tumor Thrombosis After Curative Resection.Oncologist. 2017 May;22(5):561-569. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2016-0231. Epub 2017 Apr 24. Oncologist. 2017. PMID: 28438885 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:9–29. - PubMed
-
- Lencioni R. Loco-regional treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2010;52:762–773. - PubMed
-
- Bruix J, Sala M, Llovet JM. Chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2004;127:S179–S188. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
