Growth differentiation factor-15 (GDF-15), novel biomarker for assessing atrial fibrosis in patients with atrial fibrillation and rheumatic heart disease
- PMID: 26885055
- PMCID: PMC4723900
Growth differentiation factor-15 (GDF-15), novel biomarker for assessing atrial fibrosis in patients with atrial fibrillation and rheumatic heart disease
Abstract
Objective: Growth differentiation factor-15 (GDF-15) has been identified as a strong biomarker of cardiovascular diseases; however, no evidence are available concerning the relationship of GDF-15 and atrial fibrosis in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) and rheumatic heart disease (RHD).
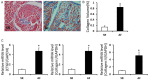
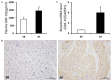
Methods: Twenty patients with rheumatic heart disease were divided into two groups, 10 cases with AF and 10 cases with sinus rhythm (SR). Clinical data and blood samples were collected; left atrial appendage was taken by the surgeon in the process of valve replacement. Masson stained sections and mRNA levels of cardiac fibrosis biomarkers were used to determine the level of cardiac fibrosis, the expression level of GDF-15 was evaluated via immunohistochemistry, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
Results: Compared with SR group, more collagen deposited in the atrial tissue of AF group. The distribution of GDF-15 in the AF group was significantly higher than SR group (P<0.05). In addition, plasma GDF-15 level and mRNA level of GDF-15 in atrial tissue of AF showed the same trend as the result of immunohistochemistry. After linear correlation analysis, the expression level of GDF-15 was found to be positively related to the degree of cardiac fibrosis.
Conclusion: GDF-15 might involve in the development and maintenance of atrial fibrosis in patients with atrial fibrillation and rheumatic heart disease, and GDF-15 could be used as a novel biomarker to evaluate myocardial fibrosis in the future.
Keywords: Growth differentiation factor-15; atrial fibrillation; atrial fibrosis; rheumatic heart disease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fibroblast growth factor-21 is positively associated with atrial fibrosis in atrial fibrillation patients with rheumatic heart disease.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Nov 1;8(11):14901-8. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26823820 Free PMC article.
-
Snail1 is positively correlated with atrial fibrosis in patients with atrial fibrillation and rheumatic heart disease.Exp Ther Med. 2017 Nov;14(5):4231-4237. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.5084. Epub 2017 Aug 31. Exp Ther Med. 2017. PMID: 29104639 Free PMC article.
-
[Relationship between FGF23/FGFR4 expression in atrial tissue and atrial fibrosis in patients with atrial fibrillation].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2018 Apr 3;98(13):1003-1007. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2018.13.010. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 29690710 Chinese.
-
Relationship between serum growth differentiation factor 15, fibroblast growth factor-23 and risk of atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Aug 4;9:899667. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.899667. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35990956 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting Value of Growth Differentiation Factor 15 and Its Correlations With Atrial Fibrillation.Heart Surg Forum. 2020 Jul 2;23(4):E452-E460. doi: 10.1532/hsf.2355. Heart Surg Forum. 2020. PMID: 32726227
Cited by
-
Serum GDF15, a Promising Biomarker in Obese Patients Undergoing Heart Surgery.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2020 Jun 24;7:103. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2020.00103. eCollection 2020. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2020. PMID: 32671100 Free PMC article.
-
Naringenin inhibits transforming growth factor-β1-induced cardiac fibroblast proliferation and collagen synthesis via G0/G1 arrest.Exp Ther Med. 2017 Nov;14(5):4425-4430. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.5103. Epub 2017 Sep 5. Exp Ther Med. 2017. PMID: 29104653 Free PMC article.
-
Novel cardiac biomarkers and multiple-marker approach in the early detection, prognosis, and risk stratification of cardiac diseases.World J Cardiol. 2025 Jul 26;17(7):106561. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i7.106561. World J Cardiol. 2025. PMID: 40741019 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomarker profile in stable Fontan patients.Int J Cardiol. 2020 Apr 15;305:56-62. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2020.01.012. Epub 2020 Jan 9. Int J Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 31959411 Free PMC article.
-
Aqueous humor protein markers in myopia: a review.Int Ophthalmol. 2024 Feb 7;44(1):21. doi: 10.1007/s10792-024-02942-z. Int Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 38324137 Review.
References
-
- Shiran A, Sagie A. Tricuspid regurgitation in mitral valve disease incidence, prognostic implications, mechanism, and management. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;53:401–408. - PubMed
-
- Hirsh BJ, Copeland-Halperin RS, Halperin JL. Fibrotic atrial cardiomyopathy, atrial fibrillation, and thromboembolism: mechanistic links and clinical inferences. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;65:2239–2251. - PubMed
-
- Andrade J, Khairy P, Dobrev D, Nattel S. The clinical profile and pathophysiology of atrial fibrillation: relationships among clinical features, epidemiology, and mechanisms. Circ Res. 2014;114:1453–1468. - PubMed
-
- Adam O, Zimmer C, Hanke N, Hartmann RW, Klemmer B, Bohm M, Laufs U. Inhibition of aldosterone synthase (CYP11B2) by torasemideprevents atrial fibrosis and atrial fibrillation in mice. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2015;85:140–150. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
