Ultrasound Assisted Extraction of Phenolic Compounds from Peaches and Pumpkins
- PMID: 26885655
- PMCID: PMC4757553
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148758
Ultrasound Assisted Extraction of Phenolic Compounds from Peaches and Pumpkins
Abstract
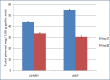
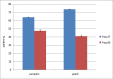
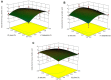
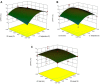
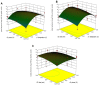
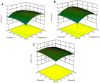
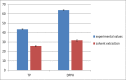
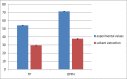
The ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) method was used to optimize the extraction of phenolic compounds from pumpkins and peaches. The response surface methodology (RSM) was used to study the effects of three independent variables each with three treatments. They included extraction temperatures (30, 40 and 50°C), ultrasonic power levels (30, 50 and 70%) and extraction times (10, 20 and 30 min). The optimal conditions for extractions of total phenolics from pumpkins were inferred to be a temperature of 41.45°C, a power of 44.60% and a time of 25.67 min. However, an extraction temperature of 40.99°C, power of 56.01% and time of 25.71 min was optimal for recovery of free radical scavenging activity (measured by 1, 1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) reduction). The optimal conditions for peach extracts were an extraction temperature of 41.53°C, power of 43.99% and time of 27.86 min for total phenolics. However, an extraction temperature of 41.60°C, power of 44.88% and time of 27.49 min was optimal for free radical scavenging activity (judged by from DPPH reduction). Further, the UAE processes were significantly better than solvent extractions without ultrasound. By electron microscopy it was concluded that ultrasonic processing caused damage in cells for all treated samples (pumpkin, peach). However, the FTIR spectra did not show any significant changes in chemical structures caused by either ultrasonic processing or solvent extraction.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Optimization of extraction of phenolics from leaves of Ficus virens.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2013 Oct;14(10):903-15. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1200365. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2013. PMID: 24101207 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of Ultrasonic-Assisted Extraction of Total Phenolics from Citrus aurantium L. Blossoms and Evaluation of Free Radical Scavenging, Anti-HMG-CoA Reductase Activities.Molecules. 2019 Jun 26;24(13):2368. doi: 10.3390/molecules24132368. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31248058 Free PMC article.
-
Radical scavenging potential of phenolics from Bryophyllum pinnatum (LAM.) OKEN.Prep Biochem Biotechnol. 2011;41(3):305-19. doi: 10.1080/10826068.2010.541314. Prep Biochem Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 21660869
-
Simultaneous Optimization of the Ultrasonic Extraction Method and Determination of the Antioxidant Activities of Hydroxysafflor Yellow A and Anhydrosafflor Yellow B from Safflower Using a Response Surface Methodology.Molecules. 2020 Mar 9;25(5):1226. doi: 10.3390/molecules25051226. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32182800 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasonic-assisted enzymatic extraction of phenolics from broccoli (Brassica oleracea L. var. italica) inflorescences and evaluation of antioxidant activity in vitro.Food Sci Technol Int. 2015 Jun;21(4):306-19. doi: 10.1177/1082013214536174. Epub 2014 May 16. Food Sci Technol Int. 2015. PMID: 24837595
Cited by
-
Microwave-Assisted Extraction of Cannabinoids in Hemp Nut Using Response Surface Methodology: Optimization and Comparative Study.Molecules. 2017 Nov 3;22(11):1894. doi: 10.3390/molecules22111894. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 29099795 Free PMC article.
-
Progress in Low-Impact Processing Technologies to Deliver More Sustainable and Healthy Food Tomorrow.Foods. 2025 Jun 30;14(13):2332. doi: 10.3390/foods14132332. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40647084 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Butterfly Pea Flower as a Novel Ingredient to Produce Antioxidant-Enriched Yellow Pea-Based Breakfast Cereals.Foods. 2022 Oct 30;11(21):3447. doi: 10.3390/foods11213447. Foods. 2022. PMID: 36360061 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Phenolic Compounds from Mango (Mangifera indica cv. Chok Anan) Peel and Its Inhibitory Effect on Enzymatic Browning of Potato Puree.Food Technol Biotechnol. 2019 Sep;57(3):350-357. doi: 10.17113/ftb.57.03.19.5728. Food Technol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31866748 Free PMC article.
-
Plants Metabolome Study: Emerging Tools and Techniques.Plants (Basel). 2021 Nov 8;10(11):2409. doi: 10.3390/plants10112409. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34834772 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ozsoy N, Can A, Yanardag R, Akev N.Antioxidant activity of Smilax excelsa L. leaf extracts. Food Chemistry 2008; 110: 571–583. 10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.02.037 - DOI
-
- Nassr-Allah AA, Aboul-Enein AM, Aboul-Enein KM, Lightfoot DA, Cocchetto A, El-Shemy H. Anti-cancer and anti-oxidant activity of some Egyptian medicinal plants. Journal of Medicinal Plants Research 2009; 3: 799–808.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

