Efficacy of Transforaminal Endoscopic Spine System (TESSYS) Technique in Treating Lumbar Disc Herniation
- PMID: 26887645
- PMCID: PMC4762298
- DOI: 10.12659/msm.894870
Efficacy of Transforaminal Endoscopic Spine System (TESSYS) Technique in Treating Lumbar Disc Herniation
Abstract
BACKGROUND To compare efficacy and safety of percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic spine system (TESSYS) and traditional fenestration discectomy (FD) in treatment of lumbar disc herniation (LDH). MATERIAL AND METHODS A total of 106 LDH patients were divided into TESSYS group (n=48) and FD group (n=58). Visual analogue scale (VAS), Oswestry disability index (ODI), Japanese Orthopedic Association (JOA), and modified MacNab criteria were used for efficacy evaluation. Post-operative responses were compared by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) based on detection of serum IL-6, CRP, and CPK levels. RESULTS In the TESSYS group, compared with the FD group, we observed, shorter incision length, less blood loss, shorter hospital stay, lower hospitalization cost, shorter recovery time, lower complication rate (all P<0.001), and lower VAS scores of lumbago and skelalgia at 3 days and 1, 3, and 6 months postoperatively (all P<0.05). At 24 and 48 h postoperatively, CRP level was remarkably higher in the FD group compared to the TESSYS group (P<0.001). Further, comparison of IL-6 levels at 6, 12, 24, and 48 h postoperatively revealed significantly higher levels in the FD group than in the FESSYS group (all P<0.001). CONCLUSIONS TESSYS had clinical advantages over FD and entails less trauma and quicker postoperative recovery, suggesting that TESSYS is well tolerated by patients and is a better approach than FD in surgical treatment of LDH.
Figures
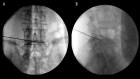
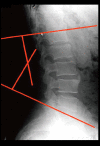
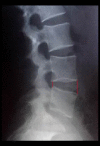
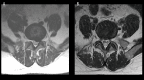
Similar articles
-
Comparison of percutaneous endoscopic transforaminal discectomy, microendoscopic discectomy, and microdiscectomy for symptomatic lumbar disc herniation: minimum 2-year follow-up results.J Neurosurg Spine. 2018 Mar;28(3):317-325. doi: 10.3171/2017.6.SPINE172. Epub 2018 Jan 5. J Neurosurg Spine. 2018. PMID: 29303471
-
Therapeutic effect of transforaminal endoscopic spine system in the treatment of prolapse of lumbar intervertebral disc.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018 Jul;22(1 Suppl):103-110. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201807_15371. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30004561 Clinical Trial.
-
[A comparison of results between percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy and fenestration discectomy for lumbar disc herniation in the adolscents].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2015 Dec 15;95(47):3852-5. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 27337804 Chinese.
-
Original Designed Uniportal-Bichannel Spinal Endoscopic System (UBiSES) for Foraminoplasty in Percutaneous Endoscopic Transforaminal Discectomy.Orthop Surg. 2021 Oct;13(7):1987-1999. doi: 10.1111/os.13050. Epub 2021 Sep 15. Orthop Surg. 2021. PMID: 34523790 Free PMC article.
-
Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy Versus Posterior Open Lumbar Microdiscectomy for the Treatment of Symptomatic Lumbar Disc Herniation: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis.World Neurosurg. 2018 Dec;120:352-362. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2018.08.236. Epub 2018 Sep 8. World Neurosurg. 2018. PMID: 30205219
Cited by
-
Comprehensive comparison of therapeutic efficacy of radiofrequency target disc decompression and nucleoplasty for lumbar disc herniation: a five year follow-up.Int Orthop. 2018 Apr;42(4):843-849. doi: 10.1007/s00264-017-3661-5. Epub 2017 Oct 31. Int Orthop. 2018. PMID: 29090325
-
The biomechanical effect on the adjacent L4/L5 segment of S1 superior facet arthroplasty: a finite element analysis for the male spine.J Orthop Surg Res. 2021 Jun 17;16(1):391. doi: 10.1186/s13018-021-02540-0. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021. PMID: 34140040 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Endoscopic Discectomy Versus Non-Endoscopic Discectomy for Symptomatic Lumbar Disc Herniation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Global Spine J. 2022 Jun;12(5):1012-1026. doi: 10.1177/21925682211020696. Epub 2021 Aug 17. Global Spine J. 2022. PMID: 34402320 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical efficacy of nucleoplasty for uncontained lumbar disc herniation: a retrospective study.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024 Jan 2;25(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s12891-023-07120-3. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024. PMID: 38166911 Free PMC article.
-
Augmented Reality Surgical Navigation in Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery: A Preclinical Study.Bioengineering (Basel). 2023 Sep 18;10(9):1094. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10091094. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37760196 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cowperthwaite MC, van den Hout WB, Webb KM. The impact of early recovery on long-term outcomes in a cohort of patients undergoing prolonged nonoperative treatment for lumbar disc herniation: clinical article. J Neurosurg Spine. 2013;19:301–6. - PubMed
-
- Wang JC, Dailey AT, Mummaneni PV, et al. Guideline update for the performance of fusion procedures for degenerative disease of the lumbar spine. Part 8: lumbar fusion for disc herniation and radiculopathy. J Neurosurg Spine. 2014;21:48–53. - PubMed
-
- Sloan TJ, Walsh DA. Explanatory and diagnostic labels and perceived prognosis in chronic low back pain. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2010;35:E1120–25. - PubMed
-
- Marshall LW, McGill SM. The role of axial torque in disc herniation. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 2010;25:6–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

