Angiotensin II-mediated hypertension impairs nitric oxide-induced NKCC2 inhibition in thick ascending limbs
- PMID: 26887831
- PMCID: PMC4835923
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00473.2015
Angiotensin II-mediated hypertension impairs nitric oxide-induced NKCC2 inhibition in thick ascending limbs
Abstract
In thick ascending limbs (THALs), nitric oxide (NO) decreases NaCl reabsorption via cGMP-mediated inhibition of Na-K-2Cl cotransporter (NKCC2). In angiotensin (ANG II)-induced hypertension, endothelin-1 (ET-1)-induced NO production by THALs is impaired. However, whether this alters NO's natriuretic effects and the mechanisms involved are unknown. In other cell types, ANG II augments phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5)-mediated cGMP degradation. We hypothesized that NO-mediated inhibition of NKCC2 activity and stimulation of cGMP synthesis are blunted via PDE5 in ANG II-induced hypertension. Sprague-Dawley rats were infused with vehicle or ANG II (200 ng·kg-1·min-1) for 5 days. ET-1 reduced NKCC2 activity by 38 ± 13% (P < 0.05) in THALs from vehicle-treated rats but not from ANG II-hypertensive rats (Δ: -9 ± 13%). A NO donor yielded similar results as ET-1. In contrast, dibutyryl-cGMP significantly decreased NKCC2 activity in both vehicle-treated and ANG II-hypertensive rats (control: Δ-44 ± 15% vs.
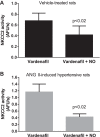
Ang ii: Δ-41 ± 10%). NO increased cGMP by 2.08 ± 0.36 fmol/μg protein in THALs from vehicle-treated rats but only 1.06 ± 0.25 fmol/μg protein in ANG II-hypertensive rats (P < 0.04). Vardenafil (25 nM), a PDE5 inhibitor, restored NO's ability to inhibit NKCC2 activity in THALs from ANG II-hypertensive rats (Δ: -60 ± 9%, P < 0.003). Similarly, NO's stimulation of cGMP was also restored by vardenafil (vehicle-treated: 1.89 ± 0.71 vs. ANG II-hypertensive: 2.02 ± 0.32 fmol/μg protein). PDE5 expression did not differ between vehicle-treated and ANG II-hypertensive rats. We conclude that NO-induced inhibition of NKCC2 and increases in cGMP are blunted in ANG II-hypertensive rats due to PDE5 activation. Defects in the response of THALs to NO may enhance NaCl retention in ANG II-induced hypertension.
Keywords: cGMP; endothelin-1; kidney; phosphodiesterase 5; sodium transport.
Copyright © 2016 the American Physiological Society.
Figures







References
-
- Aggen JB, Nairn AC, Chamberlin R. Regulation of protein phosphatase-1. Chem Biol 7: R13–23, 2000. - PubMed
-
- Bae EH, Ma SK, Lee J, Kim SW. Altered regulation of renal nitric oxide and atrial natriuretic peptide systems in angiotensin II-induced hypertension. Regul Pept 170: 31–37, 2011. - PubMed
-
- Blount MA, Beasley A, Zoraghi R, Sekhar KR, Bessay EP, Francis SH, Corbin JD. Binding of tritiated sildenafil, tadalafil, or vardenafil to the phosphodiesterase-5 catalytic site displays potency, specificity, heterogeneity, and cGMP stimulation. Mol Pharmacol 66: 144–152, 2004. - PubMed
-
- Burnier M. Angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockers. Circulation 103: 904–912, 2001. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

