The extended Infant Feeding, Activity and Nutrition Trial (InFANT Extend) Program: a cluster-randomized controlled trial of an early intervention to prevent childhood obesity
- PMID: 26888759
- PMCID: PMC4758178
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-016-2836-0
The extended Infant Feeding, Activity and Nutrition Trial (InFANT Extend) Program: a cluster-randomized controlled trial of an early intervention to prevent childhood obesity
Abstract
Background: Understanding how we can prevent childhood obesity in scalable and sustainable ways is imperative. Early RCT interventions focused on the first two years of life have shown promise however, differences in Body Mass Index between intervention and control groups diminish once the interventions cease. Innovative and cost-effective strategies seeking to continue to support parents to engender appropriate energy balance behaviours in young children need to be explored.
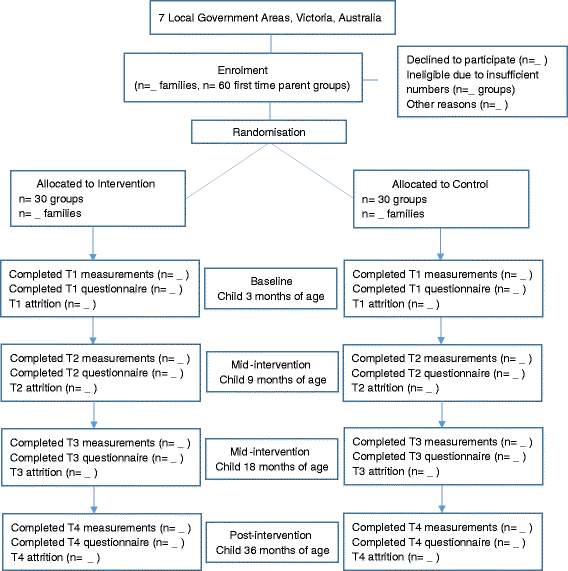
Methods/design: The Infant Feeding Activity and Nutrition Trial (InFANT) Extend Program builds on the early outcomes of the Melbourne InFANT Program. This cluster randomized controlled trial will test the efficacy of an extended (33 versus 15 month) and enhanced (use of web-based materials, and Facebook® engagement), version of the original Melbourne InFANT Program intervention in a new cohort. Outcomes at 36 months of age will be compared against the control group.
Discussion: This trial will provide important information regarding capacity and opportunities to maximize early childhood intervention effectiveness over the first three years of life. This study continues to build the evidence base regarding the design of cost-effective, scalable interventions to promote protective energy balance behaviors in early childhood, and in turn, promote improved child weight and health across the life course.
Trial registration: ACTRN12611000386932. Registered 13 April 2011.
References
-
- Chung A, Backholer K, Wong E, Palermo C, Keating C, Peeters A. Trends in child and adolescent obesity prevalence in economically advanced countries according to socioeconomic position: a systematic review. Obes Rev. 2015 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous