Histone Modification of Nedd4 Ubiquitin Ligase Controls the Loss of AMPA Receptors and Cognitive Impairment Induced by Repeated Stress
- PMID: 26888924
- PMCID: PMC4756151
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3056-15.2016
Histone Modification of Nedd4 Ubiquitin Ligase Controls the Loss of AMPA Receptors and Cognitive Impairment Induced by Repeated Stress
Abstract
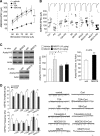
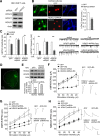
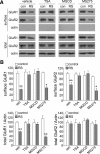
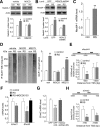
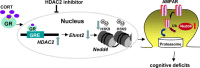
Stress and the major stress hormone corticosterone induce profound influences in the brain. Altered histone modification and transcriptional dysfunction have been implicated in stress-related mental disorders. We previously found that repeated stress caused an impairment of prefrontal cortex (PFC)-mediated cognitive functions by increasing the ubiquitination and degradation of AMPA-type glutamate receptors via a mechanism depending on the E3 ubiquitin ligase Nedd4. Here, we demonstrated that in PFC of repeatedly stressed rats, active glucocorticoid receptor had the increased binding to the glucocorticoid response element of histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC2) promoter, resulting in the upregulation of HDAC2. Inhibition or knock-down of HDAC2 blocked the stress-induced impairment of synaptic transmission, AMPAR expression, and recognition memory. Furthermore, we found that, in stressed animals, the HDAC2-dependent downregulation of histone methyltransferase Ehmt2 (G9a) led to the loss of repressive histone methylation at the Nedd4-1 promoter and the transcriptional activation of Nedd4. These results have provided an epigenetic mechanism and a potential treatment strategy for the detrimental effects of chronic stress.
Significance statement: Prolonged stress exposure can induce altered histone modification and transcriptional dysfunction, which may underlie the profound influence of stress in regulating brain functions. We report an important finding about the epigenetic mechanism controlling the detrimental effects of repeated stress on synaptic transmission and cognitive function. First, it has revealed the stress-induced alteration of key epigenetic regulators HDAC2 and Ehmt2, which determines the synaptic and behavioral effects of repeated stress. Second, it has uncovered the stress-induced histone modification of the target gene Nedd4, an E3 ligase that is critically involved in the ubiquitination and degradation of AMPA receptors and cognition. Third, it has provided the epigenetic approach, HDAC2 inhibition or knock-down, to rescue synaptic and cognitive functions in stressed animals.
Keywords: AMPA receptors; E3 ubiquitin ligase; corticosterone; histone deacetylase; histone methyltransferase; histone modification.
Copyright © 2016 the authors 0270-6474/16/362119-12$15.00/0.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Molecular and Epigenetic Mechanisms for the Complex Effects of Stress on Synaptic Physiology and Cognitive Functions.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017 Nov 1;20(11):948-955. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyx052. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 29016816 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Repeated stress causes cognitive impairment by suppressing glutamate receptor expression and function in prefrontal cortex.Neuron. 2012 Mar 8;73(5):962-77. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.12.033. Neuron. 2012. PMID: 22405206 Free PMC article.
-
Aβ-Induced Synaptic Alterations Require the E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Nedd4-1.J Neurosci. 2016 Feb 3;36(5):1590-5. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2964-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26843640 Free PMC article.
-
Nedd4-mediated AMPA receptor ubiquitination regulates receptor turnover and trafficking.J Neurochem. 2011 Oct;119(1):27-39. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07221.x. Epub 2011 Mar 17. J Neurochem. 2011. PMID: 21338354 Free PMC article.
-
Nedd4 and Nedd4-2: ubiquitin ligases at work in the neuron.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013 Mar;45(3):706-10. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2012.12.006. Epub 2012 Dec 20. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23262292 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of EHMT1/2 rescues synaptic and cognitive functions for Alzheimer's disease.Brain. 2019 Mar 1;142(3):787-807. doi: 10.1093/brain/awy354. Brain. 2019. PMID: 30668640 Free PMC article.
-
Chemogenetic Activation of Prefrontal Cortex in Shank3-Deficient Mice Ameliorates Social Deficits, NMDAR Hypofunction, and Sgk2 Downregulation.iScience. 2019 Jul 26;17:24-35. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2019.06.014. Epub 2019 Jun 11. iScience. 2019. PMID: 31247448 Free PMC article.
-
Periaqueductal Gray Glutamatergic Transmission Governs Chronic Stress-Induced Depression.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018 Jan;43(2):302-312. doi: 10.1038/npp.2017.199. Epub 2017 Aug 30. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018. PMID: 28853438 Free PMC article.
-
Dysfunction of Glutamatergic Synaptic Transmission in Depression: Focus on AMPA Receptor Trafficking.Biol Psychiatry Glob Open Sci. 2022 Mar 8;3(2):187-196. doi: 10.1016/j.bpsgos.2022.02.007. eCollection 2023 Apr. Biol Psychiatry Glob Open Sci. 2022. PMID: 37124348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular and Epigenetic Mechanisms for the Complex Effects of Stress on Synaptic Physiology and Cognitive Functions.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017 Nov 1;20(11):948-955. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyx052. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 29016816 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Blumberg HP, Leung HC, Skudlarski P, Lacadie CM, Fredericks CA, Harris BC, Charney DS, Gore JC, Krystal JH, Peterson BS. A functional magnetic resonance imaging study of bipolar disorder: state- and trait-related dysfunction in ventral prefrontal cortices. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2003;60:601–609. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.60.6.601. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
