Selective Disruption of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5-Homer Interactions Mimics Phenotypes of Fragile X Syndrome in Mice
- PMID: 26888925
- PMCID: PMC4756152
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2921-15.2016
Selective Disruption of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5-Homer Interactions Mimics Phenotypes of Fragile X Syndrome in Mice
Abstract
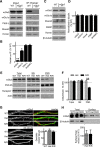
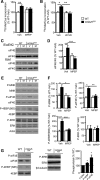
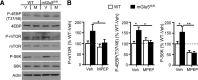
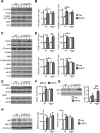
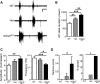
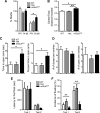
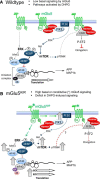
Altered function of the Gq-coupled, Group 1 metabotropic glutamate receptors, specifically mGlu5, is implicated in multiple mouse models of autism and intellectual disability. mGlu5 dysfunction has been most well characterized in the fragile X syndrome mouse model, the Fmr1 knock-out (KO) mouse, where pharmacological and genetic reduction of mGlu5 reverses many phenotypes. mGlu5 is less associated with its scaffolding protein Homer in Fmr1 KO mice, and restoration of mGlu5-Homer interactions by genetic deletion of a short, dominant negative of Homer, H1a, rescues many phenotypes of Fmr1 KO mice. These results suggested that disruption of mGlu5-Homer leads to phenotypes of FXS. To test this idea, we examined mice with a knockin mutation of mGlu5 (F1128R; mGlu5(R/R)) that abrogates binding to Homer. Although FMRP levels were normal, mGlu5(R/R) mice mimicked multiple phenotypes of Fmr1 KO mice, including reduced mGlu5 association with the postsynaptic density, enhanced constitutive mGlu5 signaling to protein synthesis, deficits in agonist-induced translational control, protein synthesis-independent LTD, neocortical hyperexcitability, audiogenic seizures, and altered behaviors, including anxiety and sensorimotor gating. These results reveal new roles for the Homer scaffolds in regulation of mGlu5 function and implicate a specific molecular mechanism in a complex brain disease.
Significance statement: Abnormal function of the metabotropic, or Gq-coupled, glutamate receptor 5 (mGlu5) has been implicated in neurodevelopmental disorders, including a genetic cause of intellectual disability and autism called fragile X syndrome. In brains of a mouse model of fragile X, mGlu5 is less associated with its binding partner Homer, a scaffolding protein that regulates mGlu5 localization to synapses and its ability to activate biochemical signaling pathways. Here we show that a mouse expressing a mutant mGlu5 that cannot bind to Homer is sufficient to mimic many of the biochemical, neurophysiological, and behavioral symptoms observed in the fragile X mouse. This work provides strong evidence that Homer-mGlu5 binding contributes to symptoms associated with neurodevelopmental disorders.
Keywords: Homer; LTD; UP states; fragile X syndrome; mGluR5; protein synthesis.
Copyright © 2016 the authors 0270-6474/16/362131-17$15.00/0.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Disrupted Homer scaffolds mediate abnormal mGluR5 function in a mouse model of fragile X syndrome.Nat Neurosci. 2012 Jan 22;15(3):431-40, S1. doi: 10.1038/nn.3033. Nat Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22267161 Free PMC article.
-
A reduced number of metabotropic glutamate subtype 5 receptors are associated with constitutive homer proteins in a mouse model of fragile X syndrome.J Neurosci. 2005 Sep 28;25(39):8908-16. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0932-05.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 16192381 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated CaMKIIα and Hyperphosphorylation of Homer Mediate Circuit Dysfunction in a Fragile X Syndrome Mouse Model.Cell Rep. 2015 Dec 15;13(10):2297-311. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.11.013. Epub 2015 Dec 6. Cell Rep. 2015. PMID: 26670047 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of group-I metabotropic glutamate (mGlu) receptor mediated signalling in disorders associated with Intellectual Disability and Autism.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2014 Oct;46 Pt 2(Pt 2):228-41. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2014.02.003. Epub 2014 Feb 15. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2014. PMID: 24548786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fragile X syndrome: a preclinical review on metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 (mGluR5) antagonists and drug development.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014 Mar;231(6):1217-26. doi: 10.1007/s00213-013-3330-3. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014. PMID: 24232444 Review.
Cited by
-
Autoimmune seizures and epilepsy.J Clin Invest. 2019 Mar 1;129(3):926-940. doi: 10.1172/JCI125178. Epub 2019 Feb 4. J Clin Invest. 2019. PMID: 30714986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CRISPR-mediated activation of autism gene Itgb3 restores cortical network excitability via mGluR5 signaling.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2022 Jul 20;29:462-480. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2022.07.013. eCollection 2022 Sep 13. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2022. PMID: 36035754 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral and Neurochemical Phenotyping of Mice Incapable of Homer1a Induction.Front Behav Neurosci. 2017 Nov 1;11:208. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2017.00208. eCollection 2017. Front Behav Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29163080 Free PMC article.
-
Updates on the Physiopathology of Group I Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors (mGluRI)-Dependent Long-Term Depression.Cells. 2023 Jun 8;12(12):1588. doi: 10.3390/cells12121588. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37371058 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Synaptic Perspective of Fragile X Syndrome and Autism Spectrum Disorders.Neuron. 2019 Mar 20;101(6):1070-1088. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2019.02.041. Neuron. 2019. PMID: 30897358 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
