The Polycomb Group Protein EZH2 Impairs DNA Damage Repair Gene Expression in Human Uterine Fibroids
- PMID: 26888970
- PMCID: PMC4829092
- DOI: 10.1095/biolreprod.115.134924
The Polycomb Group Protein EZH2 Impairs DNA Damage Repair Gene Expression in Human Uterine Fibroids
Abstract
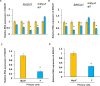
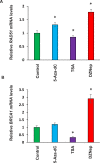
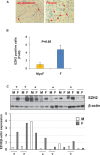
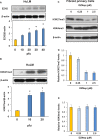
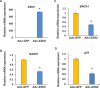
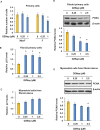
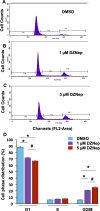
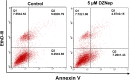
Uterine fibroids are benign, smooth muscle tumors that occur in approximately 70%-80% of women by age 50 yr. The cellular and molecular mechanism(s) by which uterine fibroids (UFs) develop are not fully understood. Accumulating evidence demonstrates that several genetic abnormalities, including deletions, rearrangements, translocations, as well as mutations, have been found in UFs. These genetic anomalies suggest that low DNA damage repair capacity may be involved in UF formation. The objective of this study was to determine whether expression levels of DNA damage repair-related genes were altered, and how they were regulated in the pathogenesis of UFs. Expression levels of DNA repair-related genes RAD51 and BRCA1 were deregulated in fibroid tissues as compared to adjacent myometrial tissues. Expression levels of chromatin protein enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) were higher in a subset of fibroids as compared to adjacent myometrial tissues by both immunohistochemistry and Western blot analysis. Treatment with an inhibitor of EZH2 markedly increased expression levels of RAD51 and BRCA1 in fibroid cells and inhibited cell proliferation paired with cell cycle arrest. Restoring the expression of RAD51 and BRCA1 by treatment with EZH2 inhibitor was dependent on reducing the enrichment of trimethylation of histone 3 lysine 27 epigenetic mark in their promoter regions. This study reveals the important role of EZH2-regulated DNA damage-repair genes via histone methylation in fibroid biology, and may provide novel therapeutic targets for the medical treatment of women with symptomatic UFs.
Keywords: BRCA1; DNA damage repair; EZH2; H3K27me3; RAD51; fibroid.
© 2016 by the Society for the Study of Reproduction, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Preliminary Study: Human Fibroid Stro-1+/CD44+ Stem Cells Isolated From Uterine Fibroids Demonstrate Decreased DNA Repair and Genomic Integrity Compared to Adjacent Myometrial Stro-1+/CD44+ Cells.Reprod Sci. 2019 May;26(5):619-638. doi: 10.1177/1933719118783252. Epub 2018 Jun 28. Reprod Sci. 2019. PMID: 29954254 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Polycomb Group Protein EZH2-Mediated DNA Mismatch Repair Gene MSH2 in Human Uterine Fibroids.Reprod Sci. 2016 Oct;23(10):1314-25. doi: 10.1177/1933719116638186. Epub 2016 Mar 31. Reprod Sci. 2016. PMID: 27036951 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol modulates epigenetic regulators of promoter histone methylation and acetylation that restores BRCA1, p53, p21CIP1 in human breast cancer cell lines.Biofactors. 2019 Sep;45(5):818-829. doi: 10.1002/biof.1544. Epub 2019 Jul 17. Biofactors. 2019. PMID: 31317586
-
Early Life Adverse Environmental Exposures Increase the Risk of Uterine Fibroid Development: Role of Epigenetic Regulation.Front Pharmacol. 2016 Mar 1;7:40. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00040. eCollection 2016. Front Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26973527 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic regulation of cancer biology and anti-tumor immunity by EZH2.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 20;7(51):85624-85640. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12928. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27793053 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Roles of the Histone Protein Modifier EZH2 in the Uterus and Placenta.Epigenomes. 2020 Sep;4(3):20. doi: 10.3390/epigenomes4030020. Epub 2020 Sep 2. Epigenomes. 2020. PMID: 33732505 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacogenomic discovery of genetically targeted cancer therapies optimized against clinical outcomes.NPJ Precis Oncol. 2024 Aug 28;8(1):186. doi: 10.1038/s41698-024-00673-z. NPJ Precis Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39198692 Free PMC article.
-
Bromodomain-Containing Protein 9 Regulates Signaling Pathways and Reprograms the Epigenome in Immortalized Human Uterine Fibroid Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 11;25(2):905. doi: 10.3390/ijms25020905. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38255982 Free PMC article.
-
A Preliminary Study: Human Fibroid Stro-1+/CD44+ Stem Cells Isolated From Uterine Fibroids Demonstrate Decreased DNA Repair and Genomic Integrity Compared to Adjacent Myometrial Stro-1+/CD44+ Cells.Reprod Sci. 2019 May;26(5):619-638. doi: 10.1177/1933719118783252. Epub 2018 Jun 28. Reprod Sci. 2019. PMID: 29954254 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancer of Zeste 2 Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 Subunit Is Required for Uterine Epithelial Integrity.Am J Pathol. 2019 Jun;189(6):1212-1225. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2019.02.016. Epub 2019 Apr 5. Am J Pathol. 2019. PMID: 30954472 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bulun SE. Uterine fibroids. N Engl J Med. 2013;369((14)):1344–1355. - PubMed
-
- Al-Hendy A, Salama S. Gene therapy and uterine leiomyoma: a review. Hum Reprod Update. 2006;12((4)):385–400. - PubMed
-
- Heinonen HR, Sarvilinna NS, Sjoberg J, Kampjarvi K, Pitkanen E, Vahteristo P, Makinen N, Aaltonen LA. MED12 mutation frequency in unselected sporadic uterine leiomyomas. Fertil Steril. 2014;102((4)):1137–1142. - PubMed
-
- Rieker RJ, Agaimy A, Moskalev EA, Hebele S, Hein A, Mehlhorn G, Beckmann MW, Hartmann A, Haller F. Mutation status of the mediator complex subunit 12 (MED12) in uterine leiomyomas and concurrent/metachronous multifocal peritoneal smooth muscle nodules (leiomyomatosis peritonealis disseminata) Pathology. 2013;45((4)):388–392. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

