Urological Manifestations of Placenta Percreta
- PMID: 26889119
- PMCID: PMC4748759
- DOI: 10.1159/000365691
Urological Manifestations of Placenta Percreta
Abstract
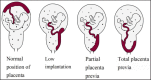
Placenta percreta is a condition of pregnancy associated with abnormal decidua placenta. It is characterized by invasion of chorionic villi past the myometrium and serosa, towards urogenital organs. Complications include massive hemorrhage, bladder dysfunction, and severe infections during delivery. Reports suggest an increasing prevalence of this condition. From a urological perspective, this review suggests how early diagnostic modalities, effective treatment plans, and appropriate surgical methods may aid in decreasing the morbidity and mortality of placenta percreta. The importance of maintaining bladder integrity during hysterectomy is emphasized.
Keywords: Abnormal placentation; Hematuria; Placenta; Placenta percreta; Post postpartum hemorrhage; Pregnancy; Shock.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Placenta percreta with bladder invasion as a cause of life threatening hemorrhage.J Urol. 2000 Oct;164(4):1270-4. J Urol. 2000. PMID: 10992378 Review.
-
Placenta percreta invading left broad ligament in a woman with twin pregnancy: A case report.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2022 Nov 15;84:104875. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2022.104875. eCollection 2022 Dec. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2022. PMID: 36582923 Free PMC article.
-
Histopathology of Placenta Creta: Chorionic Villi Intrusion into Myometrial Vascular Spaces and Extravillous Trophoblast Proliferation are Frequent and Specific Findings With Implications for Diagnosis and Pathogenesis.Int J Gynecol Pathol. 2016 Nov;35(6):497-508. doi: 10.1097/PGP.0000000000000250. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 2016. PMID: 26630223
-
Placenta percreta is associated with more frequent severe maternal morbidity than placenta accreta.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018 Aug;219(2):193.e1-193.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2018.04.049. Epub 2018 May 5. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018. PMID: 29733839
-
Placenta accreta spectrum: pathophysiology and evidence-based anatomy for prenatal ultrasound imaging.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018 Jan;218(1):75-87. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2017.05.067. Epub 2017 Jun 24. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018. PMID: 28599899 Review.
Cited by
-
Interval Hysterectomy for Placenta Percreta - a Case Report.Cent Asian J Glob Health. 2019 Feb 5;8(1):345. doi: 10.5195/cajgh.2019.345. eCollection 2019. Cent Asian J Glob Health. 2019. PMID: 30881759 Free PMC article.
-
Emergency peripartum hysterectomy at Jordan University hospital - a teaching hospital experience.Prz Menopauzalny. 2020 Jul;19(2):66-71. doi: 10.5114/pm.2020.97840. Epub 2020 Jul 13. Prz Menopauzalny. 2020. PMID: 32802016 Free PMC article.
-
Placenta percreta with bladder invasion: The armamentarium available in its management.Urol Ann. 2019 Jul-Sep;11(3):324-327. doi: 10.4103/UA.UA_84_18. Urol Ann. 2019. PMID: 31413516 Free PMC article.
-
Risk Factors for Urological Complications Associated with Caesarean Section-A Case-Control Study.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Jan 14;58(1):123. doi: 10.3390/medicina58010123. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 35056431 Free PMC article.
-
Urological issues in pregnancy: A review for urologists.Can Urol Assoc J. 2020 Oct;14(10):352-357. doi: 10.5489/cuaj.6526. Can Urol Assoc J. 2020. PMID: 32432535 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Clausen C, Lonn L, Langhoff-Roos J. Management of placenta percreta: a review of published cases. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2014;93:138–143. - PubMed
-
- Fritsch H, Lienemann A, Brenner E, Ludwikowski B. Clinical anatomy of the pelvic floor. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2004;175:1–64. - PubMed
-
- Baader B, Baader SL, Herrmann M, Stenzl A. Autonomic innervation of the female pelvis. Anatomic basis. Urologe A. 2004;43:133–140. - PubMed
-
- Jarcho J. Malformations of the uterus; review of the subject, including embryology, comparative anatomy, diagnosis and report of cases. Am J Surg. 1946;71:106–166. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous