Virological and immunological characteristics of HIV-infected individuals at the earliest stage of infection
- PMID: 26889497
- PMCID: PMC4754199
- DOI: 10.1016/S2055-6640(20)30688-9
Virological and immunological characteristics of HIV-infected individuals at the earliest stage of infection
Abstract
Background: The challenges of identifying acute HIV infection (AHI) have resulted in a lack of critical information on early AHI that constrains the development of therapeutics that are designed to eradicate HIV from the infected host.
Methods: AHI participants were recruited from the Thai Red Cross Anonymous Clinic in Bangkok, Thailand into the RV254/SEARCH010 protocol and categorised according to Fiebig stages as follows: Fiebig I (HIV-RNA+, p24 Ag-, HIV IgM-) and Fiebig II-IV (HIV-RNA+, p24 Ag + or -, HIV IgM- or +, Western blot- or indeterminate). Proviral and viral burden and immune activation levels were compared between Fiebig stage groups at the time of AHI. CD4 and CD4/CD8 ratio were also compared between groups before and up to 96 weeks of ART.
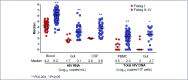
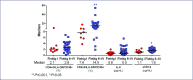
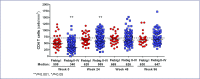
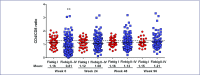
Results: Median age was 27 years and 96% were male. Fiebig I individuals had lower median HIV-DNA in mononuclear cells from blood (3 vs. 190 copies/106 cells) and gut (0 vs. 898 copies/106 cells), and lower HIV-RNA in blood (4.2 vs. 6.2 log10 copies/mL), gut (1.7 vs. 3.1 log10 copies/mg) and cerebrospinal fluid (2.0 vs. 3.8 log10 copies/mL), when compared to Fiebig II-IV individuals (all P<0.01). Median plasma sCD14 level was lower (1.1 vs. 1.6 μg/mL) in Fiebig I individuals as was the frequency of CD8+HLADR+CD38+ T cells in blood (7.6 vs. 14.9%, both P<0.05). The median plasma interleukin 6 levels were similar between stages (0.6 in Fiebig I vs. 0.5 pg/mL in Fiebig II-IV, P>0.05). The frequencies of CD4+HLA-DR+CD38+ T cells were also similar between these stages (2.1 vs. 2.6%, P>0.05). Median CD4 count and CD4/CD8 ratio were higher in Fiebig I: 508 vs. 340 cells/mm3 and 1.1 vs. 0.7, respectively (both P<0.001). After ART, CD4 cell count normalised by week 24 in Fiebig I and week 48 in Fiebig II-IV. However, CD4/CD8 ratio was lower in both groups after 96 weeks of ART compared to healthy Thais (P=0.02).
Conclusions: Compared to later AHI stages, Fiebig I was associated with lower HIV burden in blood and tissue compartments, lower immune activation and higher CD4 and CD4/CD8 ratio. ART in Fiebig I-IV resulted in normalisation of CD4 cell count within the first year, supporting the benefit of early ART. However, the CD4/CD8 ratio was not normalised after 2 years of ART in all AHI stages, suggesting some degree of persistent immunological dysfunction even when ART was instituted as early as Fiebig I.
Keywords: CD4; CD4/CD8 ratio; Fiebig I; acute HIV infection; immune activation; reservoir.
Figures
References
-
- Fiebig EW, Wright DJ, Rawal BD et al. . Dynamics of HIV viremia and antibody seroconversion in plasma donors: implications for diagnosis and staging of primary HIV infection. AIDS 2003; 17: 1871–1879. - PubMed
-
- Martin AR, Siliciano RF. Progress toward HIV eradication: case reports, current efforts, and the challenges associated with cure. Ann Rev Med 2015. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
