DREADDs for Neuroscientists
- PMID: 26889809
- PMCID: PMC4759656
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.01.040
DREADDs for Neuroscientists
Abstract
To understand brain function, it is essential that we discover how cellular signaling specifies normal and pathological brain function. In this regard, chemogenetic technologies represent valuable platforms for manipulating neuronal and non-neuronal signal transduction in a cell-type-specific fashion in freely moving animals. Designer Receptors Exclusively Activated by Designer Drugs (DREADD)-based chemogenetic tools are now commonly used by neuroscientists to identify the circuitry and cellular signals that specify behavior, perceptions, emotions, innate drives, and motor functions in species ranging from flies to nonhuman primates. Here I provide a primer on DREADDs highlighting key technical and conceptual considerations and identify challenges for chemogenetics going forward.
Keywords: DREADD; chemical biology; chemogenetic; synthetic biology.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


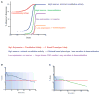
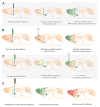
References
-
- Allen JA, Roth BL. Strategies to discover unexpected targets for drugs active at G protein-coupled receptors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2011;51:117–144. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

