Short-Term and Long-Term Reproducibility of Hypertension Phenotypes Obtained by Office and Ambulatory Blood Pressure Measurements
- PMID: 26890293
- PMCID: PMC8032105
- DOI: 10.1111/jch.12792
Short-Term and Long-Term Reproducibility of Hypertension Phenotypes Obtained by Office and Ambulatory Blood Pressure Measurements
Abstract
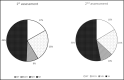
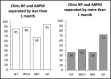
The authors aimed to assess the reproducibility of normotension and white-coat, masked, and sustained hypertension in 839 untreated patients who underwent two separate assessments (median, 3; interquartile range, 0-13 months) by both office and ambulatory blood pressure (BP) monitoring (ABPM). The proportion of patients falling into the same category in the two assessments was: 52% normotension and 55% white-coat, 47% masked, and 82% sustained hypertension. The most frequent switch was to sustained hypertension (26% of white-coat and 33% of masked hypertension). No clinical factors predicted the change in category, except for higher office diastolic BP in patients with masked hypertension who developed sustained hypertension, compared with those who remained with masked hypertension (84±4 mm Hg vs 80±5 mm Hg; P=.006). The reproducibility of hypertension phenotypes was highly dependent on the time between assessments. The authors conclude that white-coat and masked hypertension phenotypes are only reproducible in the short-term, while they frequently shift towards sustained hypertension in the long-term.
© 2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Mancia G, Fagard R, Narkiewicz K, et al. ESH/ESC Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. The Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). J Hypertens. 2013;31:1281–1357. - PubMed
-
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) . Hypertension. The clinical management of primary hypertension in adults. Clinical Guideline 127. 2011. http://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/CG127. Accessed November, 2015.
-
- O'Brien E, Parati G, Stergiou G, et al. European Society of Hypertension position paper on ambulatory blood pressure monitoring. J Hypertens. 2013;31:1731–1768. - PubMed
-
- Ohkubo T, Kikuya M, Metoki H, et al. Prognosis of “masked” hypertension and “white‐coat” hypertension detected by 24‐h ambulatory blood pressure monitoring 10‐year follow‐up from the Ohasama study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005;46:508–515. - PubMed
-
- Verdecchia P, Reboldi GP, Angeli F, et al. Short‐ and long‐term incidence of stroke in white‐coat hypertension. Hypertension. 2005;45:203–208. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

