Retrospective data suggests that the higher prevalence of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo in individuals with type 2 diabetes is mediated by hypertension
- PMID: 26890424
- PMCID: PMC4791946
- DOI: 10.3233/VES-150563
Retrospective data suggests that the higher prevalence of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo in individuals with type 2 diabetes is mediated by hypertension
Abstract
Objective: Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV) has been linked to comorbidities like diabetes and hypertension. However, the relationship between type 2 diabetes (DM) and BPPV is unclear. The purpose of this retrospective study was to examine the relationship between DM and BPPV in the presence of known contributors like age, gender and hypertension.
Methods: A retrospective review of the records of 3933 individuals was categorized by the specific vestibular diagnosis and for the presence of type 2 DM and hypertension. As the prevalence of BPPV was higher in people with type 2 DM compared to those without DM, multivariable logistic regressions were used to identify variables predictive of BPPV. The relationship between type 2 DM, hypertension and BPPV was analyzed using mediation analysis.
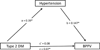
Results: BPPV was seen in 46% of individuals with type 2 DM, compared to 37% of individuals without DM (p< 0.001). Forty two percent of the association between type 2 DM and BPPV was mediated by hypertension, and supported hypertension as a complete mediator in the relationship between type 2 DM and BPPV.
Conclusions: Hypertension may provide the mediating pathway by which diabetes affects the vestibular system. Individuals with complaints of dizziness, with comorbidities including hypertension and diabetes, may benefit from a screening for BPPV.
Keywords: Type 2 Diabetes; benign paroxysmal positional vertigo; hypertension.
Figures
References
-
- Baloh RW, Honrubia V, Jacobson K. Benign positional vertigo: clinical and oculographic features in 240 cases. Neurology. 1987;37:371–378. - PubMed
-
- Baron RM, Kenny DA. The moderator-mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 1986;51:1173–1182. - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharyya N, Baugh RF, Orvidas L, Barrs D, Bronston LJ, Cass S, Chalian AA, Desmond AL, Earll JM, Fife TD, Fuller DC, Judge JO, Mann NR, Rosenfeld RM, Schuring LT, Steiner RW, Whitney SL, Haidari J. Clinical practice guideline: benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery. 2008;139:S47–S81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

