A cryoinjury model in neonatal mice for cardiac translational and regeneration research
- PMID: 26890681
- PMCID: PMC5464389
- DOI: 10.1038/nprot.2016.031
A cryoinjury model in neonatal mice for cardiac translational and regeneration research
Abstract
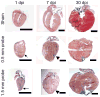
The introduction of injury models for neonatal mouse hearts has accelerated research on the mechanisms of cardiac regeneration in mammals. However, some existing models, such as apical resection and ligation of the left anterior descending artery, produce variable results, which may be due to technical difficulties associated with these methods. Here we present an alternative model for the study of cardiac regeneration in neonatal mice in which cryoinjury is used to induce heart injury. This model yields a reproducible injury size, does not induce known mechanisms of cardiac regeneration and leads to a sustained reduction of cardiac function. This protocol uses reusable cryoprobes that can be assembled in 5 min, with the entire procedure taking 15 min per pup. The subsequent heart collection and fixation takes 2 d to complete. Cryoinjury results in a myocardial scar, and the size of injury can be scaled by the use of different cryoprobes (0.5 and 1.5 mm). Cryoinjury models are medically relevant to diseases in human infants with heart disease. In summary, the myocardial cryoinjury model in neonatal mice described here is a useful tool for cardiac translational and regeneration research.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Figures





References
-
- Li F, Wang X, Capasso JM, Gerdes AM. Rapid transition of cardiac myocytes from hyperplasia to hypertrophy during postnatal development. Journal of molecular and cellular cardiology. 1996;28:1737–1746. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

