Do Microglia Default on Network Maintenance in Alzheimer's Disease?
- PMID: 26890782
- PMCID: PMC4927862
- DOI: 10.3233/JAD-151075
Do Microglia Default on Network Maintenance in Alzheimer's Disease?
Abstract
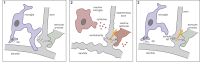
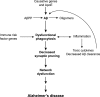
Although the cause of Alzheimer's disease (AD) remains unknown, a number of new findings suggest that the immune system may play a critical role in the early stages of the disease. Genome-wide association studies have identified a wide array of risk-associated genes for AD, many of which are associated with abnormal functioning of immune cells. Microglia are the brain's immune cells. They play an important role in maintaining the brain's extracellular environment, including clearance of aggregated proteins such as amyloid-β (Aβ). Recent studies suggest that microglia play a more active role in the brain than initially considered. Specifically, microglia provide trophic support to neurons and also regulate synapses. Microglial regulation of neuronal activity may have important consequences for AD. In this article we review the function of microglia in AD and examine the possible relationship between microglial dysfunction and network abnormalities, which occur very early in disease pathogenesis.
Keywords: Microglia; network abnormalities; neural networks; phagocytosis; synapse pruning.
Figures
References
-
- Glenner GG, Wong CW (1984) Alzheimer’s disease: Initial report of the purification and characterization of a novel cerebrovascular amyloid protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 120, 885–890. - PubMed
-
- Goldgaber D, Lerman MI, McBride OW, Saffiotti U, Gajdusek DC (1987) Characterization and chromosomal localization of a cDNA encoding brain amyloid of Alzheimer’s disease. Science 235, 877–880. - PubMed
-
- Kang J, Lemaire HG, Unterbeck A, Salbaum JM, Masters CL, Grzeschik KH, Multhaup G, Beyreuther K, Muller-Hill B (1987) The precursor of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid A4 protein resembles a cell-surface receptor. Nature 325, 733–736. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

