Association of Body Composition With Survival and Locoregional Control of Radiotherapy-Treated Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 26891703
- PMCID: PMC5080910
- DOI: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2015.6339
Association of Body Composition With Survival and Locoregional Control of Radiotherapy-Treated Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
Importance: Major weight loss is common in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) who undergo radiotherapy (RT). How baseline and posttreatment body composition affects outcome is unknown.
Objective: To determine whether lean body mass before and after RT for HNSCC predicts survival and locoregional control.
Design, setting, and participant: Retrospective study of 2840 patients with pathologically proven HNSCC undergoing curative RT at a single academic cancer referral center from October 1, 2003, to August 31, 2013. One hundred ninety patients had computed tomographic (CT) scans available for analysis of skeletal muscle (SM). The effect of pre-RT and post-RT SM depletion (defined as a CT-measured L3 SM index of less than 52.4 cm2/m2 for men and less than 38.5 cm2/m2 for women) on survival and disease control was evaluated. Final follow-up was completed on September 27, 2014, and data were analyzed from October 1, 2014, to November 29, 2015.
Main outcomes and measures: Primary outcomes were overall and disease-specific survival and locoregional control. Secondary analyses included the influence of pre-RT body mass index (BMI) and interscan weight loss on survival and recurrence.
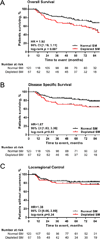
Results: Among the 2840 consecutive patients who underwent screening, 190 had whole-body positron emission tomography-CT or abdominal CT scans before and after RT and were included for analysis. Of these, 160 (84.2%) were men and 30 (15.8%) were women; their mean (SD) age was 57.7 (9.4) years. Median follow up was 68.6 months. Skeletal muscle depletion was detected in 67 patients (35.3%) before RT and an additional 58 patients (30.5%) after RT. Decreased overall survival was predicted by SM depletion before RT (hazard ratio [HR], 1.92; 95% CI, 1.19-3.11; P = .007) and after RT (HR, 2.03; 95% CI, 1.02-4.24; P = .04). Increased BMI was associated with significantly improved survival (HR per 1-U increase in BMI, 0.91; 95% CI, 0.87-0.96; P < .001). Weight loss without SM depletion did not affect outcomes. Post-RT SM depletion was more substantive in competing multivariate models of mortality risk than weight loss-based metrics (Bayesian information criteria difference, 7.9), but pre-RT BMI demonstrated the greatest prognostic value.
Conclusions and relevance: Diminished SM mass assessed by CT imaging or BMI can predict oncologic outcomes for patients with HNSCC, whereas weight loss after RT initiation does not predict SM loss or survival.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: None reported.
Figures


References
-
- Jager-Wittenaar H, Dijkstra PU, Vissink A, et al. Changes in nutritional status and dietary intake during and after head and neck cancer treatment. Head Neck. 2011;33(6):863–870. - PubMed
-
- Jackson W, Alexander N, Schipper M, Fig L, Feng F, Jolly S. Characterization of changes in total body composition for patients with head and neck cancer undergoing chemoradiotherapy using dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry. Head Neck. 2014;36(9):1356–1362. - PubMed
-
- Garg S, Yoo J, Winquist E. Nutritional support for head and neck cancer patients receiving radiotherapy: a systematic review. Support Care Cancer. 2010;18(6):667–677. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

