Gene expression in human brain implicates sexually dimorphic pathways in autism spectrum disorders
- PMID: 26892004
- PMCID: PMC4762891
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms10717
Gene expression in human brain implicates sexually dimorphic pathways in autism spectrum disorders
Abstract
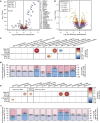
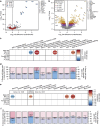
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is more prevalent in males, and the mechanisms behind this sex-differential risk are not fully understood. Two competing, but not mutually exclusive, hypotheses are that ASD risk genes are sex-differentially regulated, or alternatively, that they interact with characteristic sexually dimorphic pathways. Here we characterized sexually dimorphic gene expression in multiple data sets from neurotypical adult and prenatal human neocortical tissue, and evaluated ASD risk genes for evidence of sex-biased expression. We find no evidence for systematic sex-differential expression of ASD risk genes. Instead, we observe that genes expressed at higher levels in males are significantly enriched for genes upregulated in post-mortem autistic brain, including astrocyte and microglia markers. This suggests that it is not sex-differential regulation of ASD risk genes, but rather naturally occurring sexually dimorphic processes, potentially including neuron-glial interactions, that modulate the impact of risk variants and contribute to the sex-skewed prevalence of ASD.
Conflict of interest statement
D.H.G. serves on the scientific advisory board for SynapDx. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders 5th edn American Psychiatric Association (2013).
-
- Wingate M. et al. Prevalence of autism spectrum disorder among children aged 8 years—Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, 11 sites, United States, 2010. MMWR Surveill. Summ. 63, 1–21 (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 MH094714/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- F31MH093086/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 MH073526/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32MH073526/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- F30MH099886/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- F31 MH093086/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH100027/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 9R01MH100027/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 5R37MH060233/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R37 MH060233/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 MH089921/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01MH094714/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- F30 MH099886/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 5RC2MH089921/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

