Pharmacokinetics of oral and intravenous melatonin in healthy volunteers
- PMID: 26893170
- PMCID: PMC4759723
- DOI: 10.1186/s40360-016-0052-2
Pharmacokinetics of oral and intravenous melatonin in healthy volunteers
Abstract
Background: The aim was to investigate the pharmacokinetics of oral and iv melatonin in healthy volunteers.
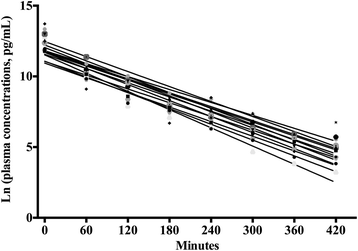
Methods: The study was performed as a cohort crossover study. The volunteers received either 10 mg oral melatonin or 10 mg intravenous melatonin on two separate study days. Blood samples were collected at different time points following oral administration and short iv infusion, respectively. Plasma melatonin concentrations were determined by RIA technique. Pharmacokinetic analyses were performed by "the method of residuals" and compartmental analysis. The pharmacokinetic variables: k a, t 1/2 absorption, t max, C max, t 1/2 elimination, AUC 0-∞, and bioavailability were determined for oral melatonin. C max, t 1/2 elimination, V d, CL and AUC 0-∞ were determined for intravenous melatonin.
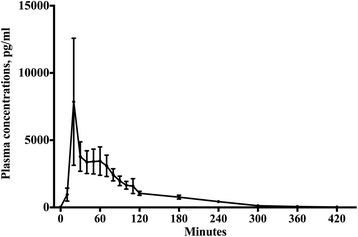
Results: Twelve male volunteers completed the study. Baseline melatonin plasma levels did not differ significantly between the study days (P = 0.067). Mean (SD) t 1/2 absorption of oral melatonin was 6.0 (3.1) min. Mean t max was 40.8 (17.8) min with a median (IQR) C max of 3550.5 (2500.5-8057.5) pg ml(-1). Mean t 1/2 elimination was 53.7 (7.0) min. Median absolute bioavailability was 2.5 (1.7-4.7) %. Median C max after short iv infusion of melatonin was 389,875.0 (174,775.0-440,362.5) pg ml(-1). Mean t 1/2 elimination was 39.4 (3.6) min, mean V d 1.2 (0.6) l kg(-1) and mean CL 0.0218 (0.0102) l min(-1) kg(-1).
Conclusions: This cohort crossover study estimated pharmacokinetics of oral and iv melatonin, respectively in healthy volunteers. Bioavailability of oral melatonin was only 3 %.
Trial registration: Eudra-CT number: 2013-000205-23 (initial registration 27.03.2013). Clinicaltrials.gov Identifier: NCT01923974 (initial registration 08.08.2013).
Figures
References
-
- Gögenur I, Kücükakin B, Panduro Jensen L, Reiter RJ, Rosenberg J. Melatonin reduces cardiac morbidity and markers of myocardial ischemia after elective abdominal aortic aneurism repair: a randomized, placebo-controlled, clinical trial. J Pineal Res. 2014;57:10–5. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12138. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous