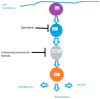
Targeting the MEK signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with RAS aberrations
- PMID: 26893312
- PMCID: PMC5933606
- DOI: 10.1177/1753465816632111
Targeting the MEK signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with RAS aberrations
Abstract
With the advancement in understanding the biology of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), therapies focused on novel molecular pathways have come to the forefront of NSCLC treatment. This review focuses on the preclinical and clinical aspects underlying the targeting of RAS aberrations in NSCLC with special focus on MEK inhibitors which work by inhibiting the principal downstream mediator of RAS aberrations with a view on how to optimize outcomes with these agents. Preclinical evidence of the activity of MEK inhibitors in KRAS-mutant NSCLC has pushed forward the clinical development of these agents (namely selumetinib and trametinib) in KRAS-mutant NSCLC particularly in combination with other agents. A number of randomized studies have been launched to confirm the activity of these agents and to establish their position in the treatment armamentarium of NSCLC.
Keywords: KRAS; MEK; lung cancer; selumetinib; trametinib.
© The Author(s), 2016.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Therapeutic potential of trametinib to inhibit the mutagenesis by inactivating the protein kinase pathway in non-small cell lung cancer.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2019 Jan;19(1):11-17. doi: 10.1080/14737140.2019.1554440. Epub 2018 Dec 4. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2019. PMID: 30513023 Review.
-
The HSP90 inhibitor, NVP-AUY922, sensitizes KRAS-mutant non-small cell lung cancer with intrinsic resistance to MEK inhibitor, trametinib.Cancer Lett. 2016 Mar 1;372(1):75-81. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.12.015. Epub 2015 Dec 23. Cancer Lett. 2016. PMID: 26723875
-
Combined use of PI3K and MEK inhibitors synergistically inhibits lung cancer with EGFR and KRAS mutations.Oncol Rep. 2016 Jul;36(1):365-75. doi: 10.3892/or.2016.4770. Epub 2016 Apr 26. Oncol Rep. 2016. PMID: 27121230
-
MEK inhibitors under development for treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2018 Jan;27(1):17-30. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2018.1415324. Epub 2017 Dec 13. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2018. PMID: 29216787 Review.
-
Selumetinib for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2017 Aug;26(8):973-984. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2017.1351543. Epub 2017 Jul 12. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2017. PMID: 28675058 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting metabolic peculiarities: a potentially novel therapeutic approach for KRAS-mutant lung cancer?J Thorac Dis. 2016 Aug;8(8):E794-5. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2016.06.72. J Thorac Dis. 2016. PMID: 27618791 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Everything Old Is New Again: Drug Repurposing Approach for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Targeting MAPK Signaling Pathway.Front Oncol. 2021 Oct 6;11:741326. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.741326. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34692523 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Personalizing Therapy Outcomes through Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathway Inhibition in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Biomedicines. 2024 Jul 5;12(7):1489. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12071489. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39062063 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selumetinib Activity in Thyroid Cancer Cells: Modulation of Sodium Iodide Symporter and Associated miRNAs.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jul 17;19(7):2077. doi: 10.3390/ijms19072077. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30018229 Free PMC article.
-
Interpreting Functional Impact of Genetic Variations by Network QTL for Genotype-Phenotype Association Study.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jan 26;9:720321. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.720321. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35155440 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdel-Rahman O., Elhalawani H., Ahmed H. (2015b) Risk of selected dermatological toxicities in cancer patients treated with MEK inhibitors: a comparative systematic review and meta-analysis. Future Oncol, in press. - PubMed
-
- Abdel-Rahman O., Elhalawani H., Ahmed H., Ellithy M. (2015c) Risk of selected gastrointestinal toxicities in cancer patients treated with MEK inhibitors: a comparative systematic review and meta-analysis. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, in press. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous