Targeting the MEK signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with RAS aberrations
- PMID: 26893312
- PMCID: PMC5933606
- DOI: 10.1177/1753465816632111
Targeting the MEK signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with RAS aberrations
Abstract
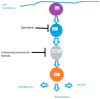
With the advancement in understanding the biology of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), therapies focused on novel molecular pathways have come to the forefront of NSCLC treatment. This review focuses on the preclinical and clinical aspects underlying the targeting of RAS aberrations in NSCLC with special focus on MEK inhibitors which work by inhibiting the principal downstream mediator of RAS aberrations with a view on how to optimize outcomes with these agents. Preclinical evidence of the activity of MEK inhibitors in KRAS-mutant NSCLC has pushed forward the clinical development of these agents (namely selumetinib and trametinib) in KRAS-mutant NSCLC particularly in combination with other agents. A number of randomized studies have been launched to confirm the activity of these agents and to establish their position in the treatment armamentarium of NSCLC.
Keywords: KRAS; MEK; lung cancer; selumetinib; trametinib.
© The Author(s), 2016.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Abdel-Rahman O., Elhalawani H., Ahmed H. (2015b) Risk of selected dermatological toxicities in cancer patients treated with MEK inhibitors: a comparative systematic review and meta-analysis. Future Oncol, in press. - PubMed
-
- Abdel-Rahman O., Elhalawani H., Ahmed H., Ellithy M. (2015c) Risk of selected gastrointestinal toxicities in cancer patients treated with MEK inhibitors: a comparative systematic review and meta-analysis. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, in press. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous