Diverse microRNAs with convergent functions regulate tumorigenesis
- PMID: 26893668
- PMCID: PMC4734215
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2015.4020
Diverse microRNAs with convergent functions regulate tumorigenesis
Abstract
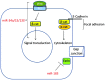
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) regulate several biological processes, including tumorigenesis. In order to comprehend the roles of miRNAs in cancer, various screens were performed to investigate the changes in the expression levels of miRNAs that occur in different types of cancer. The present review focuses on the results of five recent screens, whereby a number of overlapping miRNAs were identified to be downregulated or differentially regulated, whereas no miRNAs were observed to be frequently upregulated. Furthermore, the majority of the miRNAs that were common to >1 screen were involved in signaling networks, including wingless-related integration site, receptor tyrosine kinase and transforming growth factor-β, or in cell cycle checkpoint control. The present review will discuss the aforementioned miRNAs implicated in cell cycle checkpoint control and signaling networks.
Keywords: cancer stem cell; microRNA; microarray; signal transduction; tumorigenesis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hippocampal subregion-specific microRNA expression during epileptogenesis in experimental temporal lobe epilepsy.Neurobiol Dis. 2014 Feb;62:508-20. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2013.10.026. Epub 2013 Oct 31. Neurobiol Dis. 2014. PMID: 24184920
-
Integrated analysis of the differential cellular and EBV miRNA expression profiles in microdissected nasopharyngeal carcinoma and non-cancerous nasopharyngeal tissues.Oncol Rep. 2015 Nov;34(5):2585-601. doi: 10.3892/or.2015.4237. Epub 2015 Sep 1. Oncol Rep. 2015. PMID: 26330189
-
Construction of microRNA-messenger networks for human osteosarcoma.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Aug;234(8):14145-14153. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28107. Epub 2019 Jan 21. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30666640
-
MicroRNAs in DNA Damage Response, Carcinogenesis, and Chemoresistance.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2017;333:1-49. doi: 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2017.03.001. Epub 2017 Mar 31. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28729023 Review.
-
Tuning of major signaling networks (TGF-β, Wnt, Notch and Hedgehog) by miRNAs in human stem cells commitment to different lineages: Possible clinical application.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Jul;91:849-860. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.05.020. Epub 2017 May 11. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28501774 Review.
Cited by
-
Are circulating microRNAs peripheral biomarkers for Alzheimer's disease?Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Sep;1862(9):1617-27. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2016.06.001. Epub 2016 Jun 2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 27264337 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-130a reduces drug resistance in breast cancer.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2019 Jul 1;12(7):2699-2705. eCollection 2019. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2019. PMID: 31934100 Free PMC article.
-
miRNAs and Stem Cells as Promising Diagnostic and Therapeutic Targets for Alzheimer's Disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2023;94(s1):S203-S225. doi: 10.3233/JAD-221298. J Alzheimers Dis. 2023. PMID: 37212107 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bao B, Ali S, Ahmad A, Li Y, Banerjee S, Kong D, Aboukameel A, Mohammad R, Van Buren E, Azmi AS, Sarkar FH. Differentially expressed miRNAs in cancer-stem-like cells, Markers for tumor cell aggressiveness of pancreatic cancer. Stem Cells Dev. 2014;23:1947–1958. doi: 10.1089/scd.2013.0551. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
