Two Small Molecules Block Oral Epithelial Cell Invasion by Porphyromons gingivalis
- PMID: 26894834
- PMCID: PMC4760928
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0149618
Two Small Molecules Block Oral Epithelial Cell Invasion by Porphyromons gingivalis
Abstract
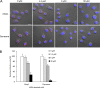
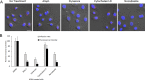
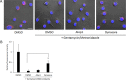
Porphyromonas gingivalis is a keystone pathogen of periodontitis. One of its bacterial characteristics is the ability to invade various host cells, including nonphagocytic epithelial cells and fibroblasts, which is known to facilitate P. gingivalis adaptation and survival in the gingival environment. In this study, we investigated two small compounds, Alop1 and dynasore, for their role in inhibition of P. gingivalis invasion. Using confocal microscopy, we showed that these two compounds significantly reduced invasion of P. gingivalis and its outer membrane vesicles into human oral keratinocytes in a dose-dependent manner. The inhibitory effects of dynasore, a dynamin inhibitor, on the bacterial entry is consistent with the notion that P. gingivalis invasion is mediated by a clathrin-mediated endocytic machinery. We also observed that microtubule arrangement, but not actin, was altered in the host cells treated with Alop1 or dynasore, suggesting an involvement of microtubule in this inhibitory activity. This work provides an opportunity to develop compounds against P. gingivalis infection.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Ximenez-Fyvie LA, Haffajee AD, Socransky SS (2000) Comparison of the microbiota of supra- and subgingival plaque in health and periodontitis. J Clin Periodontol 27: 648–657. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CA163069/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000445/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA163069/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR000445/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- G12 MD007586/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR025497/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U54 MD007586/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- R24 DA036420/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- RR0254970/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- MD007586/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- DE022428/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DE022428/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- U54MD007593/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- U54 MD007593/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- MD007593/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024975/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DA036420/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- 025332/PHS HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

