Stepwise nucleosome translocation by RSC remodeling complexes
- PMID: 26895087
- PMCID: PMC4769157
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.10051
Stepwise nucleosome translocation by RSC remodeling complexes
Abstract
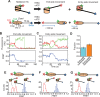
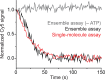
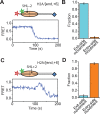
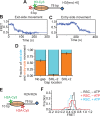
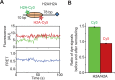
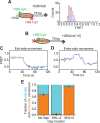
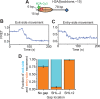
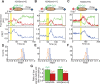
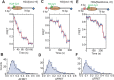
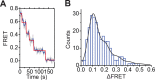
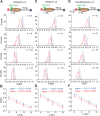
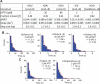
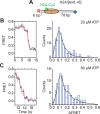
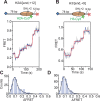
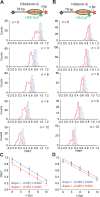
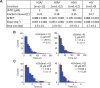
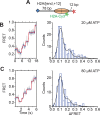
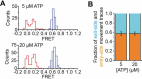
The SWI/SNF-family remodelers regulate chromatin structure by coupling the free energy from ATP hydrolysis to the repositioning and restructuring of nucleosomes, but how the ATPase activity of these enzymes drives the motion of DNA across the nucleosome remains unclear. Here, we used single-molecule FRET to monitor the remodeling of mononucleosomes by the yeast SWI/SNF remodeler, RSC. We observed that RSC primarily translocates DNA around the nucleosome without substantial displacement of the H2A-H2B dimer. At the sites where DNA enters and exits the nucleosome, the DNA moves largely along or near its canonical wrapping path. The translocation of DNA occurs in a stepwise manner, and at both sites where DNA enters and exits the nucleosome, the step size distributions exhibit a peak at approximately 1-2 bp. These results suggest that the movement of DNA across the nucleosome is likely coupled directly to DNA translocation by the ATPase at its binding site inside the nucleosome.
Keywords: FRET; RSC; S. cerevisiae; SWI/SNF; biochemistry; biophysics; chromatin; remodeling; single-molecule; structural biology.
Conflict of interest statement
XZ: Reviewing editor,
The other authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
SWI/SNF and RSC cooperate to reposition and evict promoter nucleosomes at highly expressed genes in yeast.Genes Dev. 2018 May 1;32(9-10):695-710. doi: 10.1101/gad.312850.118. Epub 2018 May 21. Genes Dev. 2018. PMID: 29785963 Free PMC article.
-
The core histone N-terminal domains are required for multiple rounds of catalytic chromatin remodeling by the SWI/SNF and RSC complexes.Biochemistry. 1999 Feb 23;38(8):2514-22. doi: 10.1021/bi982109d. Biochemistry. 1999. PMID: 10029546
-
Coordinated Action of Nap1 and RSC in Disassembly of Tandem Nucleosomes.Mol Cell Biol. 2016 Aug 12;36(17):2262-71. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00195-16. Print 2016 Sep 1. Mol Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27273866 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay among ATP-Dependent Chromatin Remodelers Determines Chromatin Organisation in Yeast.Biology (Basel). 2020 Jul 25;9(8):190. doi: 10.3390/biology9080190. Biology (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32722483 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spanning the gap: unraveling RSC dynamics in vivo.Curr Genet. 2021 Jun;67(3):399-406. doi: 10.1007/s00294-020-01144-1. Epub 2021 Jan 23. Curr Genet. 2021. PMID: 33484328 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dynamic 1D Search and Processive Nucleosome Translocations by RSC and ISW2 Chromatin Remodelers.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 15:2023.06.13.544671. doi: 10.1101/2023.06.13.544671. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Elife. 2024 Mar 18;12:RP91433. doi: 10.7554/eLife.91433. PMID: 38293098 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Mechanisms of ATP-Dependent Chromatin Remodeling Motors.Annu Rev Biophys. 2016 Jul 5;45:153-81. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biophys-051013-022819. Annu Rev Biophys. 2016. PMID: 27391925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PlantCHRs: A comprehensive database of plant chromatin remodeling factors.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023 Oct 5;21:4974-4987. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2023.10.005. eCollection 2023. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023. PMID: 37867975 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the RSC complex bound to the nucleosome.Science. 2019 Nov 15;366(6467):838-843. doi: 10.1126/science.aay0033. Epub 2019 Oct 31. Science. 2019. PMID: 31672915 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of histone chaperone Nap1 and histone acetylation in regulating phase-separation of chromatin arrays.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 15:2025.05.09.653121. doi: 10.1101/2025.05.09.653121. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40463029 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

