Use of integrin alpha 6 transcripts in a stool mRNA assay for the detection of colorectal cancers at curable stages
- PMID: 26895101
- PMCID: PMC4924744
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.7407
Use of integrin alpha 6 transcripts in a stool mRNA assay for the detection of colorectal cancers at curable stages
Abstract
Objective: An important criterion for colorectal cancer (CRC) screening is the ability to detect lesions at a curable stage. In the present study, we have assessed the integrin α6 subunit transcript (ITGA6) as part of a stool assay for the detection of colorectal lesions.
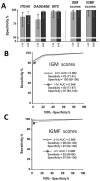
Results: In comparison with control samples, ITGA6 levels were found to be significantly increased at all stages (P < 0.01). Receiver operating characteristic analysis revealed areas under the curve of 0.89 for the prediction of CRC with 81% sensitivity and 88% specificity and of 0.90 for the prediction of advanced adenomas (Ad) with 75% sensitivity and 88% specificity. The ITGA6A variant was also found to be increased relative to ITGA6 in stage II and III CRCs. Combining ITGA6 with other selected transcripts and/or immunochemical fecal occult blood test (iFOBT) results further increased sensitivity and specificity for the detection of colorectal lesions.
Patients and methods: ITGA6 detection used alone and under various combinations including detection of other mRNA markers and iFOBT was assessed on stool samples obtained from 175 patients (91 CRCs, 24 Ad and 60 healthy controls).
Conclusions: These data confirm the usefulness and reliability of an mRNA stool assay for the detection of colorectal lesions. The validation of additional candidate genes and their analysis in multiplex qPCR represents a powerful and robust approach that can be combined with iFOBT results to improve the detection of colorectal lesions.
Keywords: adenomas; biomarker; colorectal cancer; mRNA; non-invasive screening.
Conflict of interest statement
JFB and EH are among inventors of a patented technology related to integrin α6. The other authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Droplet digital PCR for quantification of ITGA6 in a stool mRNA assay for the detection of colorectal cancers.World J Gastroenterol. 2017 Apr 28;23(16):2891-2898. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i16.2891. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28522907 Free PMC article.
-
A Stool Multitarget mRNA Assay for the Detection of Colorectal Neoplasms.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1765:217-227. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7765-9_14. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29589311
-
Investigation of MicroRNA-21 Expression Levels in Serum and Stool as a Potential Non-Invasive Biomarker for Diagnosis of Colorectal Cancer.Iran Biomed J. 2017 Mar;21(2):106-13. doi: 10.18869/acadpub.ibj.21.2.106. Epub 2016 Jul 19. Iran Biomed J. 2017. PMID: 27432735 Free PMC article.
-
Stool DNA methylation assays in colorectal cancer screening.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Sep 21;21(35):10057-61. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i35.10057. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26401070 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic value of aberrant gene methylation in stool samples for colorectal cancer or adenomas: a meta-analysis.Panminerva Med. 2015 Jun;57(2):55-64. Epub 2014 Sep 26. Panminerva Med. 2015. PMID: 25256821 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrin α6β4 in Colorectal Cancer: Expression, Regulation, Functional Alterations and Use as a Biomarker.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Dec 21;12(1):41. doi: 10.3390/cancers12010041. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31877793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrin α6-Targeted Positron Emission Tomography Imaging of Colorectal Cancer.ACS Omega. 2019 Sep 11;4(13):15560-15566. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.9b01920. eCollection 2019 Sep 24. ACS Omega. 2019. PMID: 31572857 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatic screen with clinical validation for the identification of novel stool based mRNA biomarkers for the detection of colorectal lesions including advanced adenoma.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 11;15(1):29397. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-13074-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40789879 Free PMC article.
-
Multitarget Stool mRNA Test for Detecting Colorectal Cancer Lesions Including Advanced Adenomas.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 11;13(6):1228. doi: 10.3390/cancers13061228. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33799738 Free PMC article.
-
Droplet digital PCR for quantification of ITGA6 in a stool mRNA assay for the detection of colorectal cancers.World J Gastroenterol. 2017 Apr 28;23(16):2891-2898. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i16.2891. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28522907 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62:10–29. - PubMed
-
- Willyard C. Screening: Early alert. Nature. 2015;521:S4–5. - PubMed
-
- Robertson DJ, Imperiale TF. Stool Testing for Colorectal Cancer Screening. Gastroenterology. 2015;149:1286–1293. - PubMed
-
- Maratt JK, Saini SD. Colorectal cancer screening in the 21st century: where do we go from here? Am J Manag Care. 2015;21:e447–449. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

