miR-486-5p expression pattern in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, gastric cancer and its prognostic value
- PMID: 26895105
- PMCID: PMC4941281
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.7417
miR-486-5p expression pattern in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, gastric cancer and its prognostic value
Abstract
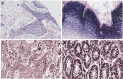
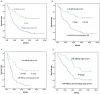
Micro RNA (miR)-486-5p is often aberrantly expressed in human cancers. The aim of this study was to identify the prognostic value of miR-486-5p expression in digestive system cancers. Tissue microarrays were constructed with 680 samples including 185 esophageal squamous cell carcinomas (ESCCs), 90 gastric adenocarcinomas (GCs), and 60 digestive system cancer tissues from 10 ESCC, 10 GC, 10 colon, 10 rectum, 10 liver, 10 pancreatic cancer, and corresponding normal tissues. Twenty normal digestive system mucosa tissues from healthy volunteers were included as normal controls. In GC, miR-486-5p expression was decreased in 62.8% of cases (59/94), increased in 33.0% (31/94), and unchanged in 4.2% (4/94); in ESCC its expression was decreased in 66.2% (129/195), increased in 32.3% (63/195), and unchanged in 1.5% (3/195). Expression of miR-486-5p was decreased in 12, and increased in 8, of 20 cases of colon or rectum cancer; decreased in 6, and increased in 4, of 10 cases of liver cancer; and decreased in 8, and increased in 2, of 10 cases of pancreatic cancer. Multivariate and univariate regression analysis demonstrated that low/unchanged miR-486-5p predicted poor prognosis in ESCC (hazard ratio [HR], 4.32; 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.62-7.14; P < 0.001; HR, 3.88; 95% CI, 2.43-6.22; P < 0.001, respectively) and GC (HR, 2.46; 95% CI, 1.35-4.50; P = 0.003; HR, 2.55; 95% CI, 1.39-4.69; P = 0.002, respectively). MiR-486-5p might therefore be an independent tumor marker for evaluating prognosis in patients with ESCC or GC.
Keywords: digestive system cancers; esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; gastric adenocarcinoma; micro RNA-486-5p; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical value of miR-425-5p detection and its association with cell proliferation and apoptosis of gastric cancer.Pathol Res Pract. 2017 Aug;213(8):929-937. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2017.05.009. Epub 2017 May 31. Pathol Res Pract. 2017. PMID: 28647207
-
Expression and prognostic value of miR-486-5p in patients with gastric adenocarcinoma.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 20;10(3):e0119384. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119384. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25793394 Free PMC article.
-
miR-675-5p enhances tumorigenesis and metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by targeting REPS2.Oncotarget. 2016 May 24;7(21):30730-47. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8950. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27120794 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Value of MicroRNAs in Esophageal Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis.Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2018 Nov 13;9(11):203. doi: 10.1038/s41424-018-0070-z. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 30420592 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic significance of circulating microRNA-21 expression in esophageal, pancreatic and colorectal cancers; a systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Surg. 2018 Dec;60:41-47. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2018.10.030. Epub 2018 Oct 15. Int J Surg. 2018. PMID: 30336280
Cited by
-
Expression of uc.189 and its clinicopathologic significance in gynecological cancers.Oncotarget. 2017 Dec 29;9(7):7453-7463. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.23761. eCollection 2018 Jan 26. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29484123 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-486 as an effective biomarker in cancer diagnosis and prognosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Oncotarget. 2018 Jan 12;9(17):13948-13958. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.24189. eCollection 2018 Mar 2. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 29568407 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA Expression in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma and Asbestosis: A Pilot Study.Dis Markers. 2017;2017:9645940. doi: 10.1155/2017/9645940. Epub 2017 Jul 3. Dis Markers. 2017. PMID: 28757678 Free PMC article.
-
miR-486-3p, miR-139-5p, and miR-21 as Biomarkers for the Detection of Oral Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Biomark Cancer. 2017 Nov 7;9:1179299X1700900001. doi: 10.1177/1179299X1700900001. eCollection 2017. Biomark Cancer. 2017. PMID: 35237086 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic and microRNA Expression Profiles Identify Biomarkers for Predicting Neo-Chemoradiotherapy Response in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinomas (ESCC).Front Pharmacol. 2021 Apr 15;12:626972. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.626972. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33935718 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87–108. - PubMed
-
- Tran GD, Sun XD, Abnet CC, Fan JH, Dawsey SM, Dong ZW, Mark SD, Qiao YL, Taylor PR. Prospective study of risk factors for esophageal and gastric cancers in the Linxian general population trial cohort in China. Int J Cancer. 2005;113:456–463. - PubMed
-
- Islami F, Kamangar F, Aghcheli K, Fahimi S, Semnani S, Taghavi N, Marjani HA, Merat S, Nasseri-Moghaddam S, Pourshams A, Nouraie M, Khatibian M, Abedi B, Brazandeh MH, Ghaziani R, Sotoudeh M, et al. Epidemiologic features of upper gastrointestinal tract cancers in Northeastern Iran. Br J Cancer. 2004;90:1402–1406. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

