Pathway of PPAR-gamma coactivators in thermogenesis: a pivotal traditional Chinese medicine-associated target for individualized treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 26895106
- PMCID: PMC4941284
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.7419
Pathway of PPAR-gamma coactivators in thermogenesis: a pivotal traditional Chinese medicine-associated target for individualized treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
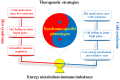
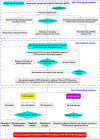
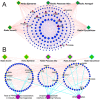
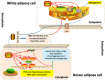
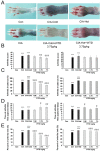
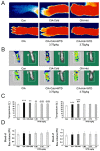
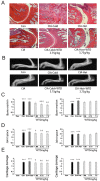
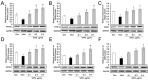
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) syndromes have been regarded as the crucial clinical manifestations for individualized diagnosis and treatment of complex diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and cancer. Especially, RA patients are classified into cold and hot syndromes with different clinical manifestations, interventions and molecular mechanisms. Better effectiveness of a classic cold syndrome-specific herbal formula Wu-tou decoction (WTD) has been achieved. To explore molecular mechanisms of syndrome-specific formulae is of great clinical significance to improve the effectiveness and pertinence of treatment for the complex diseases with personalized conditions. However, the scientific basis of WTD treatment on RA with the cold syndrome remains unclear. Here, we predicted the putative targets for composite compounds contained in WTD using drugCIPHER-CS and constructed a WTD herbs-putative targets-RA related genes network. Next, a list of major WTD targets was identified based on their topological features, including the degree, node betweenness, closeness and k-coreness in the above pharmacological network. Importantly, pathway enrichment analysis revealed that these major WTD targets were significantly associated with the pathway of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)-gamma (PPAR-γ) coactivators in thermogenesis. These computational findings were subsequently verified by experiments on a rat model of collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) with cold or hot syndromes, and on human fibroblast-like synoviocytes-rheumatoid arthritis (HFLS-RA) cell line. In conclusion, the pathway of PPAR-γ coactivators in thermogenesis might be one of the potential pharmacological targets of WTD to alleviate RA with the TCM cold syndrome. These findings may open new avenues for designing individualized treatment regimens for RA patients.
Keywords: PPAR-gamma; individualized treatment; network pharmacology; rheumatoid arthritis; traditional Chinese medicine syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors do not have any conflict of interest with the content of the manuscript.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Uncovering pharmacological mechanisms of Wu-tou decoction acting on rheumatoid arthritis through systems approaches: drug-target prediction, network analysis and experimental validation.Sci Rep. 2015 Mar 30;5:9463. doi: 10.1038/srep09463. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25820382 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring and characterizing a novel combination of paeoniflorin and talatizidine for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.Pharmacol Res. 2020 Mar;153:104658. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104658. Epub 2020 Jan 27. Pharmacol Res. 2020. PMID: 32001347
-
Wutou decoction ameliorates experimental rheumatoid arthritis via regulating NF-kB and Nrf2: Integrating efficacy-oriented compatibility of traditional Chinese medicine.Phytomedicine. 2021 May;85:153522. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153522. Epub 2021 Feb 20. Phytomedicine. 2021. PMID: 33799223
-
Wutou decoction: A latest review on molecular mechanisms, clinical studies, quality control, pharmacokinetic studies, pharmacological effects, toxicity, and target prediction.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Feb 11;341:119307. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.119307. Epub 2024 Dec 30. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39743182 Review.
-
The treatment of rheumatoid arthritis using Chinese medicinal plants: From pharmacology to potential molecular mechanisms.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Dec 24;176:177-206. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.10.010. Epub 2015 Oct 22. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26471289 Review.
Cited by
-
TCMNPAS: a comprehensive analysis platform integrating network formulaology and network pharmacology for exploring traditional Chinese medicine.Chin Med. 2024 Mar 22;19(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s13020-024-00924-y. Chin Med. 2024. PMID: 38519956 Free PMC article.
-
Traditional Chinese Medicine Aconiti Radix Cocta Improves Rheumatoid Arthritis via Suppressing COX-1 and COX-2.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Sep 7;2021:5523870. doi: 10.1155/2021/5523870. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34539799 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective Potential of Gentongping in Rat Model of Cervical Spondylotic Radiculopathy Targeting PPAR-γ Pathway.J Immunol Res. 2017;2017:9152960. doi: 10.1155/2017/9152960. Epub 2017 Nov 5. J Immunol Res. 2017. PMID: 29230425 Free PMC article.
-
Wutou decoction attenuates rheumatoid arthritis by modulating the Ahr/LOC101928120/SHC1 pathway.Pharm Biol. 2021 Dec;59(1):811-822. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2021.1941131. Pharm Biol. 2021. PMID: 34184948 Free PMC article.
-
A network pharmacology-based strategy deciphers the underlying molecular mechanisms of Qixuehe Capsule in the treatment of menstrual disorders.Chin Med. 2017 Aug 21;12:23. doi: 10.1186/s13020-017-0145-x. eCollection 2017. Chin Med. 2017. PMID: 28835770 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lu AP, Jiang M, Zhang C, Chan K. An integrative approach of linking traditional Chinese medicine syndrome classification and biomedicine diagnosis. J Ethnopharmacol. 2012;141:549–56. - PubMed
-
- Alraek T. Designing Clinical Studies That Take into Account Traditional East Asian Medicine's Systems and Methods-with Focus on Syndrome Identification. Chin J Integr Med. 2014;20:332–5. - PubMed
-
- Li S. Advances in TCM symptomatology of rheumatoid arthritis. J Tradit Chin Med. 2002;22:137–42. - PubMed
-
- He YT, Ou AH, Yang XB, Chen W, Fu LY, Lu AP, Yan XP, Feng XH, Su L, Song YJ, Zeng SP, Liu W, Qian X, et al. Traditional Chinese medicine versus western medicine as used in China in the management of rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized, single-blind, 24-week study. Rheumatol Int. 2014;34:1647–55. - PubMed
-
- Que SW. The curative effect of rheumtoid arthritis by aconitum decoction. Clinical Journal of Chinese Medicine [In Chinese] 2010;2:43–44.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

