HMGA1-pseudogenes and cancer
- PMID: 26895108
- PMCID: PMC5053758
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.7427
HMGA1-pseudogenes and cancer
Abstract
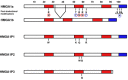
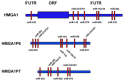
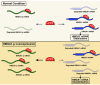
Pseudogenes are DNA sequences with high homology to the corresponding functional gene, but, because of the accumulation of various mutations, they have lost their initial functions to code for proteins. Consequently, pseudogenes have been considered until few years ago dysfunctional relatives of the corresponding ancestral genes, and then useless in the course of genome evolution. However, several studies have recently established that pseudogenes are owners of key biological functions. Indeed, some pseudogenes control the expression of functional genes by competitively binding to the miRNAs, some of them generate small interference RNAs to negatively modulate the expression of functional genes, and some of them even encode functional mutated proteins. Here, we concentrate our attention on the pseudogenes of the HMGA1 gene, that codes for the HMGA1a and HMGA1b proteins having a critical role in development and cancer progression. In this review, we analyze the family of HMGA1 pseudogenes through three aspects: classification, characterization, and their possible function and involvement in cancer.
Keywords: HMGA; cancer; ceRNA; pseudogenes.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Mighell AJ, Smith NR, Robinson PA, Markham AF. Vertebrate pseudogenes. FEBS Letters. 2000;468:109–14. - PubMed
-
- Balakirev ES, Ayala FJ. Pseudogenes: are they or functional DNA? Annu Rev Genet. 2003;37:123–51. - PubMed
-
- Loguercio LL, Wilkins TA. Structural analysis of a hmg-coA-reductase pseudogene: Insights into evolutionary processes affecting the hmgr gene family in allotetraploid cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) Curr Genet. 1998;34:241–9. - PubMed
-
- Ochman H, Davalos L. The nature and dynamics of bacterial genomes. Science. 2006;311:1730–3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

