Repurposing auranofin for the treatment of cutaneous staphylococcal infections
- PMID: 26895605
- PMCID: PMC4792765
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2015.12.016
Repurposing auranofin for the treatment of cutaneous staphylococcal infections
Abstract
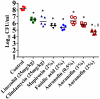
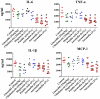
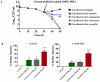
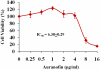
The scourge of multidrug-resistant bacterial infections necessitates the urgent development of novel antimicrobials to address this public health challenge. Drug repurposing is a proven strategy to discover new antimicrobial agents; given that these agents have undergone extensive toxicological and pharmacological analysis, repurposing is an effective method to reduce the time, cost and risk associated with traditional antibiotic innovation. In this study, the in vitro and in vivo antibacterial activities of an antirheumatic drug, auranofin, was investigated against multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. The results indicated that auranofin possesses potent antibacterial activity against all tested strains of S. aureus, including meticillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA), vancomycin-intermediate S. aureus (VISA) and vancomycin-resistant S. aureus (VRSA), with minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) ranging from 0.0625μg/mL to 0.125μg/mL. In vivo, topical auranofin proved superior to conventional antimicrobials, including fusidic acid and mupirocin, in reducing the mean bacterial load in infected wounds in a murine model of MRSA skin infection. In addition to reducing the bacterial load, topical treatment of auranofin greatly reduced the production of inflammatory cytokines, including tumour necrosis factor-α (TNFα), interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), in infected skin lesions. Moreover, auranofin significantly disrupted established in vitro biofilms of S. aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis, more so than the traditional antimicrobials linezolid and vancomycin. Taken together, these results support that auranofin has potential to be repurposed as a topical antimicrobial agent for the treatment of staphylococcal skin and wound infections.
Keywords: Auranofin; Inflammatory cytokines; Multidrug resistance; Repurposing; Topical antimicrobials.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier B.V. and the International Society of Chemotherapy. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Antibacterial activity and therapeutic efficacy of Fl-P(R)P(R)P(L)-5, a cationic amphiphilic polyproline helix, in a mouse model of staphylococcal skin infection.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Oct 22;9:5749-54. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S94505. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 26543355 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of topical and systemic antibiotic treatment of meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a murine superficial skin wound infection model.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2013 Sep;42(3):272-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2013.05.008. Epub 2013 Jul 6. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2013. PMID: 23837927
-
Repurposing ebselen for treatment of multidrug-resistant staphylococcal infections.Sci Rep. 2015 Jun 26;5:11596. doi: 10.1038/srep11596. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26111644 Free PMC article.
-
Fusidic acid in skin infections and infected atopic eczema.G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2014 Aug;149(4):453-9. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2014. PMID: 25068235 Review.
-
Clinical relevance of mupirocin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus.J Hosp Infect. 2013 Dec;85(4):249-56. doi: 10.1016/j.jhin.2013.09.006. Epub 2013 Sep 21. J Hosp Infect. 2013. PMID: 24144552 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of short synthetic antimicrobial peptides for treatment of drug-resistant and intracellular Staphylococcus aureus.Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 11;6:29707. doi: 10.1038/srep29707. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27405275 Free PMC article.
-
Auranofin Releasing Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Polyurethane Intravascular Catheter Coatings.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 Feb 28;9:37. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00037. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30873389 Free PMC article.
-
MRSA decolonization failure-are biofilms the missing link?Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2017 Mar 28;6:32. doi: 10.1186/s13756-017-0192-1. eCollection 2017. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2017. PMID: 28360994 Free PMC article.
-
Auranofin exerts antibacterial activity against Neisseria gonorrhoeae in a female mouse model of genital tract infection.PLoS One. 2022 Apr 21;17(4):e0266764. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0266764. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35446884 Free PMC article.
-
Repurposing Auranofin, an Anti-Rheumatic Gold Compound, to Treat Acne Vulgaris by Targeting the NLRP3 Inflammasome.Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2020 Sep 1;28(5):437-442. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2020.004. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2020. PMID: 32319265 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stryjewski ME, Chambers HF. Skin and soft-tissue infections caused by community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;46(Suppl 5):S368–77. - PubMed
-
- del Rio A, Cervera C, Moreno A, Moreillon P, Miro JM. Patients at risk of complications of Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;48(Suppl 4):S246–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

