The BBaRTS Healthy Teeth Behaviour Change Programme for preventing dental caries in primary school children: study protocol for a cluster randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 26897029
- PMCID: PMC4761186
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-016-1226-3
The BBaRTS Healthy Teeth Behaviour Change Programme for preventing dental caries in primary school children: study protocol for a cluster randomised controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Oral health behaviours such as establishing twice-daily toothbrushing and sugar control intake need parental self-efficacy (PSE) to prevent the development of childhood dental caries. A previous study has shown that behaviour change techniques (BCTs) delivered via a storybook can improve parental self-efficacy to undertake twice-daily toothbrushing.
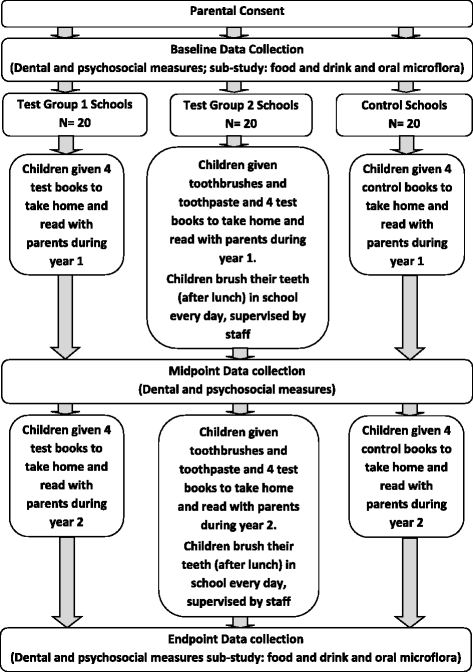
Objective: to determine whether an intervention (BBaRTS, Bedtime Brush and Read Together to Sleep), designed to increase PSE; delivered through storybooks with embedded BCTs, parenting skills and oral health messages, can improve child oral health compared to (1) an exactly similar intervention containing no behaviour change techniques, and (2) the BBaRTS intervention supplemented with home supply of fluoride toothpaste and supervised toothbrushing on schooldays.
Methods/design: A 2-year, three-arm, multicentre, cluster randomised controlled trial.
Participants: children (estimated 2000-2600) aged 5-7 years and their families from 60 UK primary schools.
Intervention: Test group 1: a series of eight children's storybooks developed by a psychologist, public health dentist, science educator, children's author and illustrators, with guidance from the Department for Education (England). The books feature animal characters and contain embedded dental health messages, parenting skills and BCTs to promote good oral health routines focused on controlling sugar intake and toothbrushing, as well as reading at bedtime. Books are given out over 2 years. Test group 2: as Test group 1 plus home supplies of fluoride toothpaste (1000 ppmF), and daily supervised toothbrushing in school on schooldays. Active Control group: series of eight books with exactly the same stories, characters and illustrations, but without BCTs, dental health messages or parenting skills. Annual child dental examinations and parental questionnaires will be undertaken. A sub-set of participants will be invited to join an embedded study of the child's diet and salivary microbiota composition.
Primary outcome measure: dental caries experience in permanent teeth at age 7-8 years.
Discussion: A multi-disciplinary team was established to develop the BBaRTS Children's Healthy Teeth Programme. The books were developed in partnership with the Department for Education (England), informed by a series of focus groups with children, teachers and parents.
Trial registration: ISRCTN21461006 (date of registration 23 September 2015).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Behaviour change intervention (education and text) to prevent dental caries in secondary school pupils: BRIGHT RCT, process and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Sep;28(52):1-142. doi: 10.3310/JQTA2103. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39258962 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Brushing RemInder 4 Good oral HealTh (BRIGHT) trial: does an SMS behaviour change programme with a classroom-based session improve the oral health of young people living in deprived areas? A study protocol of a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2019 Jul 23;20(1):452. doi: 10.1186/s13063-019-3538-6. Trials. 2019. PMID: 31337437 Free PMC article.
-
An intervention programme to establish regular toothbrushing: understanding parents' beliefs and motivating children.Int Dent J. 2000;Suppl Creating A Successful:312-23. doi: 10.1111/j.1875-595x.2000.tb00581.x. Int Dent J. 2000. PMID: 11197192 Clinical Trial.
-
More than clean teeth! Identifying factors that contribute to the development of early childhood caries.Evid Based Dent. 2024 Jun;25(2):87-88. doi: 10.1038/s41432-024-01009-3. Epub 2024 May 13. Evid Based Dent. 2024. PMID: 38740974
-
Supervised toothbrushing programs in primary schools and early childhood settings: A scoping review.Community Dent Health. 2017 Dec 1;34(4):208-225. doi: 10.1922/CDH_4057Dickson-Swift18. Community Dent Health. 2017. PMID: 29119741
Cited by
-
Use of Water by Schoolchildren: Impact of Indirectly Supervised Daily Toothbrushing-A Pilot Study.Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2020 Sep-Oct;13(5):513-517. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-1800. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2020. PMID: 33623340 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Health Promotion Interventions on Early Childhood Caries Prevention in Children Aged 2-5 Years Receiving Dental Treatment Under General Anesthesia.Front Public Health. 2020 Feb 26;8:6. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2020.00006. eCollection 2020. Front Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32175299 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Behaviour change intervention (education and text) to prevent dental caries in secondary school pupils: BRIGHT RCT, process and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Sep;28(52):1-142. doi: 10.3310/JQTA2103. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39258962 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Evaluation of the Effectiveness of a Primary Preventive Dental Health Education Programme Implemented Through School Teachers for Primary School Children in Mysore City.J Int Soc Prev Community Dent. 2017 Mar-Apr;7(2):82-89. doi: 10.4103/jispcd.JISPCD_326_16. Epub 2017 Mar 29. J Int Soc Prev Community Dent. 2017. PMID: 28462175 Free PMC article.
-
Bedtime Oral Hygiene Behaviours, Dietary Habits and Children's Dental Health.Children (Basel). 2021 May 19;8(5):416. doi: 10.3390/children8050416. Children (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34069504 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Office for National Statistics. Children’s dental health in the United Kingdom, 2003. In: London: National Statistics; 2005
-
- Department of Health, British Association for the Study of Community Dentistry: delivering better oral health: an evidence-based toolkit for prevention. In: 2nd ed. 2009.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical