Cardiomyopathy With Restrictive Physiology in Sickle Cell Disease
- PMID: 26897687
- PMCID: PMC4788530
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2015.05.013
Cardiomyopathy With Restrictive Physiology in Sickle Cell Disease
Abstract
Objectives: The aim of this study was to identify a unifying cardiac pathophysiology that explains the cardiac pathological features in sickle cell disease (SCD).
Background: Cardiopulmonary complications, the leading cause of adult death in SCD, are associated with heart chamber dilation, diastolic dysfunction, elevated tricuspid regurgitant jet velocity (TRV), and pulmonary hypertension. However, no unifying cardiac pathophysiology has been identified to explain these findings.
Methods: In a 2-part study, we first examined patients with SCD who underwent screening echocardiography during steady state at our institution. We then conducted a meta-analysis of cardiac studies in SCD.
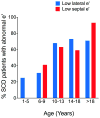
Results: In the 134 patients with SCD studied (median age 11 years), significant enlargement of the left atrial volume was present (z-score 3.1, p = 0.002), shortening fraction was normal (37.6 ± 4.7%), and lateral and septal ratios of mitral velocity to early diastolic velocity of the mitral annulus (E/e') were severely abnormal in 8% and 14% of patients, respectively, indicating impaired diastolic function. Both TRV and lateral E/e' correlated with enlarged left atrial volume in SCD (p = 0.003 and p = 0.006, respectively). Meta-analysis of 68 studies confirmed significant left atrial diameter enlargement in patients with SCD compared with controls, evidence of diastolic dysfunction and enlarged left ventricular end-diastolic dimension with normal shortening fraction. The majority of patients with catheter-confirmed pulmonary hypertension had mild pulmonary venous hypertension consistent with restrictive cardiac physiology.
Conclusions: Patients with SCD have a unique form of cardiomyopathy with restrictive physiology that is superimposed on hyperdynamic physiology and is characterized by diastolic dysfunction, left atrial dilation, and normal systolic function. This combination results in mild, secondary, pulmonary venous hypertension and elevated TRV. Sudden death is common in other forms of restrictive cardiomyopathy. Our finding of this unique restrictive cardiomyopathy may explain the increased mortality rates and sudden death seen in patients with SCD with mildly elevated TRV.
Keywords: cardiomyopathy; pulmonary hypertension; restrictive physiology; sickle cell disease.
Copyright © 2016 American College of Cardiology Foundation. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
Sickle Cardiomyopathy: The Missing Forest in the Trees.JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2016 Mar;9(3):253-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2015.06.024. Epub 2016 Feb 17. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2016. PMID: 26897663 No abstract available.
-
High-Output Heart Failure in Sickle Cell Anemia.JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2016 Sep;9(9):1122-1123. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2016.04.004. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2016. PMID: 27609152 No abstract available.
-
The Authors Reply.JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2016 Sep;9(9):1123-1124. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2016.05.010. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2016. PMID: 27609153 No abstract available.
References
-
- Gladwin MT, Sachdev V, Jison ML, et al. Pulmonary hypertension as a risk factor for death in patients with sickle cell disease. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:886–95. - PubMed
-
- Parent F, Bachir D, Inamo J, et al. A hemodynamic study of pulmonary hypertension in sickle cell disease. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:44–53. - PubMed
-
- Sachdev V, Kato GJ, Gibbs JS, et al. Echocardiographic markers of elevated pulmonary pressure and left ventricular diastolic dysfunction are associated with exercise intolerance in adults and adolescents with homozygous sickle cell anemia in the United States and United Kingdom. Circulation. 2011;124:1452–60. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

