Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Lung: Clinico-Pathologic Features, Treatment, and Outcomes
- PMID: 26898325
- PMCID: PMC5474315
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cllc.2016.01.003
Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Lung: Clinico-Pathologic Features, Treatment, and Outcomes
Abstract
Background: Large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (LCNEC) accounts for approximately 3% of lung cancers. Pathologic classification and optimal therapies are debated. We report the clinicopathologic features, treatment and survival of a series of patients with stage IV LCNEC.
Materials and methods: Cases of pathologically-confirmed stage IV LCNEC evaluated at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center from 2006 to 2013 were identified. We collected demographic, treatment, and survival data. Available radiology was evaluated by Response Evaluation Criteria In Solid Tumors (RECIST) 1.1 criteria.
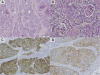
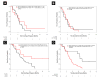
Results: Forty-nine patients with stage IV LCNEC were identified. The median age was 64 years, 63% of patients were male, and 88% were smokers. Twenty-three patients (n = 23/49; 47%) had brain metastases, 17 at diagnosis and 6 during the disease course. Seventeen LCNEC patients (35%) had molecular testing, of which 24% had KRAS mutations (n = 4/17). Treatment data for first-line metastatic disease was available on 37 patients: 70% (n = 26) received platinum/etoposide and 30% (n = 11) received other regimens. RECIST was completed on 23 patients with available imaging; objective response rate was 37% (95% confidence interval, 16%-62%) with platinum/etoposide, while those treated with other first-line regimens did not achieve a response. Median overall survival was 10.2 months (95% confidence interval, 8.6-16.4 months) for the entire cohort.
Conclusion: Patients with stage IV LCNEC have a high incidence of brain metastases. KRAS mutations are common. Patients with stage IV LCNEC do not respond as well to platinum/etoposide compared with historic data for extensive stage small-cell lung cancer; however, the prognosis is similar. Prospective studies are needed to define optimum therapy for stage IV LCNEC.
Keywords: Brain metastases; KRAS mutation; Platinum-etoposide chemotherapy; Small cell lung carcinoma; Stage IV.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have stated that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Travis WD, Linnoila RI, Tsokos MG, et al. Neuroendocrine tumors of the lung with proposed criteria for large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma. An ultrastructural, immunohistochemical, and flow cytometric study of 35 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1991;15:529–53. - PubMed
-
- Rekhtman N. Neuroendocrine tumors of the lung: an update. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2010;134:1628–38. - PubMed
-
- Travis WD, Rush W, Flieder DB, et al. Survival analysis of 200 pulmonary neuroendocrine tumors with clarification of criteria for atypical carcinoid and its separation from typical carcinoid. Am J Surg Pathol. 1998;22:934–44. - PubMed
-
- Travis WD, Brambilla E, Muller-Hermelink HK, et al. Pathology and Genetics: Tumours of the Lung, Pleura, Thymus and Heart. Lyon: IARC; 2004.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

