Distinct effects of ketamine and acetyl L-carnitine on the dopamine system in zebrafish
- PMID: 26898327
- PMCID: PMC4924529
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ntt.2016.02.004
Distinct effects of ketamine and acetyl L-carnitine on the dopamine system in zebrafish
Abstract
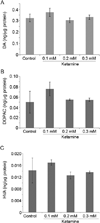
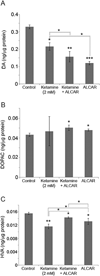
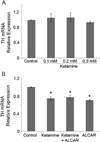
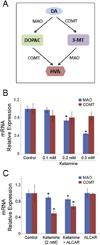
Ketamine, a noncompetitive N-methyl-D-aspartic acid (NMDA) receptor antagonist is commonly used as a pediatric anesthetic. We have previously shown that acetyl L-carnitine (ALCAR) prevents ketamine toxicity in zebrafish embryos. In mammals, ketamine is known to modulate the dopaminergic system. NMDA receptor antagonists are considered as promising anti-depressants, but the exact mechanism of their function is unclear. Here, we measured the levels of dopamine (DA) and its metabolites, 3, 4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC) and homovanillic acid (HVA), in the zebrafish embryos exposed to ketamine in the presence and absence of 0.5 mM ALCAR. Ketamine, at lower doses (0.1-0.3 mM), did not produce significant changes in DA, DOPAC or HVA levels in 52 h post-fertilization embryos treated for 24 h. In these embryos, tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) mRNA expression remained unchanged. However, 2 mM ketamine (internal embryo exposure levels equivalent to human anesthetic plasma concentration) significantly reduced DA level and TH mRNA indicating that DA synthesis was adversely affected. In the presence or absence of 2 mM ketamine, ALCAR showed similar effects on DA level and TH mRNA, but increased DOPAC level compared to control. ALCAR reversed 2 mM ketamine-induced reduction in HVA levels. With ALCAR alone, the expression of genes encoding the DA metabolizing enzymes, MAO (monoamine oxidase) and catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT), was not affected. However, ketamine altered MAO mRNA expression, except at the 0.1 mM dose. COMT transcripts were reduced in the 2 mM ketamine-treated group. These distinct effects of ketamine and ALCAR on the DA system may shed some light on the mechanism on how ketamine can work as an anti-depressant, especially at sub-anesthetic doses that do not affect DA metabolism and suppress MAO gene expression.
Keywords: Acetyl l-carnitine; Dopamine; Ketamine; MAO; Tyrosine hydroxylase; Zebrafish.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Acetyl L-carnitine targets adenosine triphosphate synthase in protecting zebrafish embryos from toxicities induced by verapamil and ketamine: An in vivo assessment.J Appl Toxicol. 2017 Feb;37(2):192-200. doi: 10.1002/jat.3340. Epub 2016 May 18. J Appl Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 27191126 Free PMC article.
-
Opposing effects of ketamine and acetyl L-carnitine on the serotonergic system of zebrafish.Neurosci Lett. 2015 Oct 21;607:17-22. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2015.09.006. Epub 2015 Sep 10. Neurosci Lett. 2015. PMID: 26365406 Free PMC article.
-
Coadministration of β-asarone and levodopa increases dopamine in rat brain by accelerating transformation of levodopa: a different mechanism from Madopar.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2014 Sep;41(9):685-90. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.12270. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24910244
-
Ethanol concentration induces production of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid and homovanillic acid in mouse brain through activation of monoamine oxidase pathway.Neurosci Lett. 2022 Jun 21;782:136689. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2022.136689. Epub 2022 May 19. Neurosci Lett. 2022. PMID: 35598694
-
Effects of bifenthrin exposure on the estrogenic and dopaminergic pathways in zebrafish embryos and juveniles.Environ Toxicol Chem. 2018 Jan;37(1):236-246. doi: 10.1002/etc.3951. Epub 2017 Nov 2. Environ Toxicol Chem. 2018. PMID: 28815728
Cited by
-
Preventive Role of L-Carnitine and Balanced Diet in Alzheimer's Disease.Nutrients. 2020 Jul 3;12(7):1987. doi: 10.3390/nu12071987. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32635400 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analgesic and Antidepressant Effects of the Clinical Glutamate Modulators Acetyl-L-Carnitine and Ketamine.Front Neurosci. 2021 May 11;15:584649. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.584649. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34045938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acetyl L-carnitine targets adenosine triphosphate synthase in protecting zebrafish embryos from toxicities induced by verapamil and ketamine: An in vivo assessment.J Appl Toxicol. 2017 Feb;37(2):192-200. doi: 10.1002/jat.3340. Epub 2016 May 18. J Appl Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 27191126 Free PMC article.
-
Nifedipine toxicity is exacerbated by acetyl l-carnitine but alleviated by low-dose ketamine in zebrafish in vivo.J Appl Toxicol. 2020 Feb;40(2):257-269. doi: 10.1002/jat.3901. Epub 2019 Oct 9. J Appl Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 31599005 Free PMC article.
-
N-acetylcysteine prevents ketamine-induced adverse effects on development, heart rate and monoaminergic neurons in zebrafish.Neurosci Lett. 2018 Aug 24;682:56-61. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2018.06.014. Epub 2018 Jun 8. Neurosci Lett. 2018. PMID: 29890257 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aalto S, Ihalainen J, Hirvonen J, Kajander J, Scheinin H, Tanila H, Nagren K, Vilkman H, Gustafsson LL, Syvalahti E, et al. Cortical glutamate-dopamine interaction and ketamine-induced psychotic symptoms in man. Psychopharmacology. 2005;182:375–383. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed AA, Ma W, Ni Y, Zhou Q, Zhao R. Embryonic exposure to corticosterone modifies aggressive behavior through alterations of the hypothalamic pituitary adrenal axis and the serotonergic system in the chicken. Horm. Behav. 2014;65:97–105. - PubMed
-
- Ali SF, David SN, Newport GD. Age-related susceptibility to MPTP-induced neurotoxicity in mice. Neurotoxicology. 1993;14:29–34. - PubMed
-
- Aroni F, Iacovidou N, Dontas I, Pourzitaki C, Xanthos T. Pharmacological aspects and potential new clinical applications of ketamine: reevaluation of an old drug. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2009;49:957–964. - PubMed
-
- Beal MF. Bioenergetic approaches for neuroprotection in Parkinson's disease. Ann. Neurol. 2003;53(Suppl. 3):S39–S47. (discussion S47-8) - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

