The impact of blood flow rate during hemodialysis on all-cause mortality
- PMID: 26898596
- PMCID: PMC5094923
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2015.111
The impact of blood flow rate during hemodialysis on all-cause mortality
Abstract
Background/aims: Inadequacy of dialysis is associated with morbidity and mortality in chronic hemodialysis (HD) patients. Blood flow rate (BFR) during HD is one of the important determinants of increasing dialysis dose. However, the optimal BFR is unclear. In this study, we investigated the impact of the BFR on all-cause mortality in chronic HD patients.
Methods: Prevalent HD patients were selected from Clinical Research Center registry for end-stage renal disease cohort in Korea. We categorized patients into two groups by BFR < 250 and ≥ 250 mL/min according to the median value of BFR 250 mL/min in this study. The primary outcome was all-cause mortality.
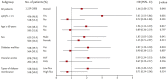
Results: A total of 1,129 prevalent HD patients were included. The number of patients in the BFR < 250 mL/min was 271 (24%) and in the BFR ≥ 250 mL/min was 858 (76%). The median follow-up period was 30 months. Kaplan-Meier analysis showed that the mortality rate was significantly higher in patients with BFR < 250 mL/min than those with BFR ≥ 250 mL/min (p = 0.042, log-rank). In the multivariate Cox regression analyses, patients with BFR < 250 mL/min had higher all-cause mortality than those with BFR ≥ 250 mL/min (hazard ratio, 1.66; 95% confidence interval, 1.00 to 2.73; p = 0.048).
Conclusions: Our data showed that BFR < 250 mL/min during HD was associated with higher all-cause mortality in chronic HD patients.
Keywords: Blood flow rate; Dialysis adequacy; Mortality; Renal dialysis.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures


References
-
- Held PJ, Port FK, Wolfe RA, et al. The dose of hemodialysis and patient mortality. Kidney Int. 1996;50:550–556. - PubMed
-
- Mandolfo S, Borlandelli S, Ravani P, Imbasciati E. How to improve dialysis adequacy in patients with vascular access problems. J Vasc Access. 2006;7:53–59. - PubMed
-
- Singh S, Choi P, Power A, et al. Ten-year patient survival on maintenance haemodialysis: association with treatment time and dialysis dose. J Nephrol. 2013;26:763–770. - PubMed
-
- Hassell DR, van der Sande FM, Kooman JP, Tordoir JP, Leunissen KM. Optimizing dialysis dose by increasing blood flow rate in patients with reduced vascular-access flow rate. Am J Kidney Dis. 2001;38:948–955. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
