PAX6 Isoforms, along with Reprogramming Factors, Differentially Regulate the Induction of Cornea-specific Genes
- PMID: 26899008
- PMCID: PMC4761963
- DOI: 10.1038/srep20807
PAX6 Isoforms, along with Reprogramming Factors, Differentially Regulate the Induction of Cornea-specific Genes
Abstract
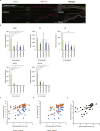
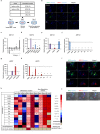
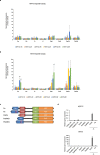
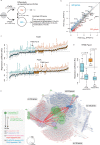
PAX6 is the key transcription factor involved in eye development in humans, but the differential functions of the two PAX6 isoforms, isoform-a and isoform-b, are largely unknown. To reveal their function in the corneal epithelium, PAX6 isoforms, along with reprogramming factors, were transduced into human non-ocular epithelial cells. Herein, we show that the two PAX6 isoforms differentially and cooperatively regulate the expression of genes specific to the structure and functions of the corneal epithelium, particularly keratin 3 (KRT3) and keratin 12 (KRT12). PAX6 isoform-a induced KRT3 expression by targeting its upstream region. KLF4 enhanced this induction. A combination of PAX6 isoform-b, KLF4, and OCT4 induced KRT12 expression. These new findings will contribute to furthering the understanding of the molecular basis of the corneal epithelium specific phenotype.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Human aniridia limbal epithelial cells lack expression of keratins K3 and K12.Exp Eye Res. 2018 Feb;167:100-109. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2017.11.005. Epub 2017 Nov 21. Exp Eye Res. 2018. PMID: 29162348
-
Direct Reprogramming Into Corneal Epithelial Cells Using a Transcriptional Network Comprising PAX6, OVOL2, and KLF4.Cornea. 2019 Nov;38 Suppl 1:S34-S41. doi: 10.1097/ICO.0000000000002074. Cornea. 2019. PMID: 31403532 Review.
-
Transcriptional profiles along cell programming into corneal epithelial differentiation.Exp Eye Res. 2021 Jan;202:108302. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2020.108302. Epub 2020 Oct 21. Exp Eye Res. 2021. PMID: 33098888
-
PAX6 regulates human corneal epithelium cell identity.Exp Eye Res. 2017 Jan;154:30-38. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2016.11.005. Epub 2016 Nov 3. Exp Eye Res. 2017. PMID: 27818314
-
PAX6 Alternative Splicing and Corneal Development.Stem Cells Dev. 2018 Mar 15;27(6):367-377. doi: 10.1089/scd.2017.0283. Epub 2018 Feb 21. Stem Cells Dev. 2018. PMID: 29343211 Review.
Cited by
-
Corneal epithelial development and homeostasis.Differentiation. 2023 Jul-Aug;132:4-14. doi: 10.1016/j.diff.2023.02.002. Epub 2023 Mar 1. Differentiation. 2023. PMID: 36870804 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Long Noncoding RNA Paupar Modulates PAX6 Regulatory Activities to Promote Alpha Cell Development and Function.Cell Metab. 2019 Dec 3;30(6):1091-1106.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2019.09.013. Epub 2019 Oct 10. Cell Metab. 2019. PMID: 31607563 Free PMC article.
-
HCE-T cell line lacks cornea-specific differentiation markers compared to primary limbal epithelial cells and differentiated corneal epithelium.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2020 Mar;258(3):565-575. doi: 10.1007/s00417-019-04563-0. Epub 2020 Jan 11. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 31927639
-
Repairing the corneal epithelium using limbal stem cells or alternative cell-based therapies.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2018 May;18(5):505-513. doi: 10.1080/14712598.2018.1443442. Epub 2018 Mar 6. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2018. PMID: 29471701 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Vivo Evaluation of PAX6 Overexpression and NMDA Cytotoxicity to Stimulate Proliferation in the Mouse Retina.Sci Rep. 2018 Dec 7;8(1):17700. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-35884-5. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30531887 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Glaser T., Walton D. S. & Maas R. L. Genomic structure, evolutionary conservation and aniridia mutations in the human PAX6 gene. Nat Genet 2, 232–239 (1992). - PubMed
-
- Walther C. & Gruss P. Pax-6, a murine paired box gene, is expressed in the developing CNS. Development 113, 1435–1449 (1991). - PubMed
-
- Epstein J. A. et al. Two independent and interactive DNA-binding subdomains of the Pax6 paired domain are regulated by alternative splicing. Genes Dev 8, 2022–2034 (1994). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

