VEGF stimulates intramembranous bone formation during craniofacial skeletal development
- PMID: 26899202
- PMCID: PMC4875795
- DOI: 10.1016/j.matbio.2016.02.005
VEGF stimulates intramembranous bone formation during craniofacial skeletal development
Abstract
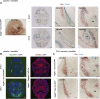
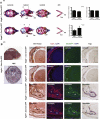
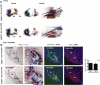
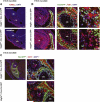
Deficiency of vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF) has been associated with severe craniofacial anomalies in both humans and mice. Cranial neural crest cell (NCC)-derived VEGF regulates proliferation, vascularization and ossification of cartilage and membranous bone. However, the function of VEGF derived from specific subpopulations of NCCs in controlling unique aspects of craniofacial morphogenesis is not clear. In this study a conditional knockdown strategy was used to genetically delete Vegfa expression in Osterix (Osx) and collagen II (Col2)-expressing NCC descendants. No major defects in calvaria and mandibular morphogenesis were observed upon knockdown of VEGF in the Col2(+) cell population. In contrast, loss of VEGF in Osx(+) osteoblast progenitor cells led to reduced ossification of calvarial and mandibular bones without affecting the formation of cartilage templates in newborn mice. The early stages of ossification in the developing jaw revealed decreased initial mineralization levels and a reduced thickness of the collagen I (Col1)-positive bone template upon loss of VEGF in Osx(+) precursors. Increased numbers of proliferating cells were detected within the jaw mesenchyme of mutant embryos. Explant culture assays revealed that mandibular osteogenesis occurred independently of paracrine VEGF action and vascular development. Reduced VEGF expression in mandibles coincided with increased phospho-Smad1/5 (P-Smad1/5) levels and bone morphogenetic protein 2 (Bmp2) expression in the jaw mesenchyme. We conclude that VEGF derived from Osx(+) osteoblast progenitor cells is required for optimal ossification of developing mandibular bones and modulates mechanisms controlling BMP-dependent specification and expansion of the jaw mesenchyme.
Keywords: Bone development; Calvaria; Craniofacial ossification; Mandible; Osterix; VEGF.
Copyright © 2016 International Society of Matrix Biology. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Cranial neural crest deletion of VEGFa causes cleft palate with aberrant vascular and bone development.Cell Tissue Res. 2015 Sep;361(3):711-22. doi: 10.1007/s00441-015-2150-7. Epub 2015 Mar 12. Cell Tissue Res. 2015. PMID: 25759071
-
Transcriptional regulation of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) by osteoblast-specific transcription factor Osterix (Osx) in osteoblasts.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jan 13;287(3):1671-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.288472. Epub 2011 Nov 22. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22110141 Free PMC article.
-
Neural crest cell-derived VEGF promotes embryonic jaw extension.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 May 12;112(19):6086-91. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1419368112. Epub 2015 Apr 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25922531 Free PMC article.
-
The roles of vascular endothelial growth factor in bone repair and regeneration.Bone. 2016 Oct;91:30-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2016.06.013. Epub 2016 Jun 25. Bone. 2016. PMID: 27353702 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of vascular endothelial growth factor in ossification.Int J Oral Sci. 2012 Jun;4(2):64-8. doi: 10.1038/ijos.2012.33. Int J Oral Sci. 2012. PMID: 22722639 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Fell-Muir Lecture: Regulatory mechanisms of skeletal and connective tissue development and homeostasis - lessons from studies of human disorders.Int J Exp Pathol. 2016 Aug;97(4):296-302. doi: 10.1111/iep.12198. Epub 2016 Sep 1. Int J Exp Pathol. 2016. PMID: 27581728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Atf4 regulates angiogenic differences between alveolar bone and long bone macrophages by regulating M1 polarization, based on single-cell RNA sequencing, RNA-seq and ATAC-seq analysis.J Transl Med. 2023 Mar 14;21(1):193. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04046-1. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 36918894 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Frontier Development of Alveolar Bone Grafting on Orthodontic Tooth Movement.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Jun 30;10:869191. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.869191. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35845390 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ETV2 regulating PHD2-HIF-1α axis controls metabolism reprogramming promotes vascularized bone regeneration.Bioact Mater. 2024 Mar 22;37:222-238. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.02.014. eCollection 2024 Jul. Bioact Mater. 2024. PMID: 38549772 Free PMC article.
-
It Takes Two to Tango: Coupling of Angiogenesis and Osteogenesis for Bone Regeneration.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2017 Nov 3;5:68. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2017.00068. eCollection 2017. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 29164110 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chai Y, Maxson RE., Jr. Recent advances in craniofacial morphogenesis. Dev. Dyn. 2006;235:2353–2375. - PubMed
-
- Weston JA, Thiery JP. Pentimento: neural crest and the origin of mesectoderm. Dev. Biol. 2015;401:37–61. - PubMed
-
- Stalmans I, Lambrechts D, De Smet F, Jansen S, Wang J, Maity S, Kneer P, von der Ohe M, Swillen A, Maes C, Gewillig M, Molin DG, Hellings P, Boetel T, Haardt M, Compernolle V, Dewerchin M, Plaisance S, Vlietinck R, Emanuel B, Gittenberger-de Groot AC, Scambler P, Morrow B, Driscol DA, Moons L, Esguerra CV, Carmeliet G, Behn-Krappa A, Devriendt K, Collen D, Conway SJ, Carmeliet P. VEGF: a modifier of the del22q11 (DiGeorge) syndrome? Nat. Med. 2003;9:173–182. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

