The challenge of improving boiling: lessons learned from a randomized controlled trial of water pasteurization and safe storage in Peru
- PMID: 26899531
- PMCID: PMC9150588
- DOI: 10.1017/S0950268816000236
The challenge of improving boiling: lessons learned from a randomized controlled trial of water pasteurization and safe storage in Peru
Abstract
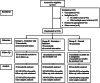
Boiling is the most common method of household water treatment in developing countries; however, it is not always effectively practised. We conducted a randomized controlled trial among 210 households to assess the effectiveness of water pasteurization and safe-storage interventions in reducing Escherichia coli contamination of household drinking water in a water-boiling population in rural Peru. Households were randomized to receive either a safe-storage container or a safe-storage container plus water pasteurization indicator or to a control group. During a 13-week follow-up period, households that received a safe-storage container and water pasteurization indicator did not have a significantly different prevalence of stored drinking-water contamination relative to the control group [prevalence ratio (PR) 1·18, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0·92-1·52]. Similarly, receipt of a safe-storage container alone had no effect on prevalence of contamination (PR 1·02, 95% CI 0·79-1·31). Although use of water pasteurization indicators and locally available storage containers did not increase the safety of household drinking water in this study, future research could illuminate factors that facilitate the effective use of these interventions to improve water quality and reduce the risk of waterborne disease in populations that boil drinking water.
Keywords: Epidemiology; Escherichia coli (E. coli); Water (quality); Water (safe).
Figures

Similar articles
-
"Improved" But Not Necessarily Safe: An Assessment of Fecal Contamination of Household Drinking Water in Rural Peru.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2015 Sep;93(3):501-8. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.14-0802. Epub 2015 Jul 20. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2015. PMID: 26195455 Free PMC article.
-
Field efficacy evaluation and post-treatment contamination risk assessment of an ultraviolet disinfection and safe storage system.Water Res. 2015 Nov 15;85:74-84. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2015.08.013. Epub 2015 Aug 8. Water Res. 2015. PMID: 26302217
-
Microbiologic effectiveness of boiling and safe water storage in South Sulawesi, Indonesia.J Water Health. 2011 Sep;9(3):577-85. doi: 10.2166/wh.2011.255. J Water Health. 2011. PMID: 21976204
-
Effects of source- versus household contamination of tubewell water on child diarrhea in rural Bangladesh: a randomized controlled trial.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 27;10(3):e0121907. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121907. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25816342 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Microbial Water Quality at the Point of Use: The Role of Socio-Economic Factors and Water Handling Practices in Kitwe District, Zambia.Environ Health Insights. 2025 May 18;19:11786302251337563. doi: 10.1177/11786302251337563. eCollection 2025. Environ Health Insights. 2025. PMID: 40391106 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Associations of Boiled Water and Lifespan Water Sources With Mortality: A Cohort Study of 33,467 Older Adults.Front Public Health. 2022 Jun 27;10:921738. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.921738. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35832269 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of the Feasibility and Acceptability of Using Water Pasteurization Indicators to Increase Access to Safe Drinking Water in the Peruvian Amazon.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2020 Jul;103(1):455-464. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.18-0963. Epub 2020 Apr 30. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2020. PMID: 32372750 Free PMC article.
-
Health Trade-Offs of Boiling Drinking Water with Solid Fuels: A Modeling Study.Environ Health Perspect. 2025 Jun;133(6):67021. doi: 10.1289/EHP15059. Epub 2025 Jun 23. Environ Health Perspect. 2025. PMID: 40344151 Free PMC article.
-
Household-level risk factors for water contamination and antimicrobial resistance in drinking water among households with children under 5 in rural San Marcos, Cajamarca, Peru.One Health. 2023 Jan 3;16:100482. doi: 10.1016/j.onehlt.2023.100482. eCollection 2023 Jun. One Health. 2023. PMID: 36655146 Free PMC article.
-
Fecal Contamination of Drinking Water Was Associated with Diarrheal Pathogen Carriage among Children Younger than 5 Years in Three Peruvian Rural Communities.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2020 Jun;102(6):1279-1285. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.19-0337. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2020. PMID: 32207402 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu L, et al. Global, regional, and national causes of child mortality in 2000–13, with projections to inform post-2015 priorities: an updated systematic analysis. Lancet 2015; 385: 430–440. - PubMed
-
- WHO/UNICEF. Diarrhoea: why children are still dying and what can be done. Geneva: WHO, 2009.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

