Ultrasound triggered image-guided drug delivery to inhibit vascular reconstruction via paclitaxel-loaded microbubbles
- PMID: 26899550
- PMCID: PMC4761943
- DOI: 10.1038/srep21683
Ultrasound triggered image-guided drug delivery to inhibit vascular reconstruction via paclitaxel-loaded microbubbles
Abstract
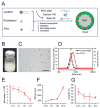
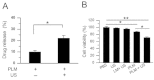
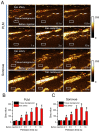
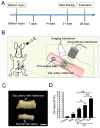
Paclitaxel (PTX) has been recognized as a promising drug for intervention of vascular reconstructions. However, it is still difficult to achieve local drug delivery in a spatio-temporally controllable manner under real-time image guidance. Here, we introduce an ultrasound (US) triggered image-guided drug delivery approach to inhibit vascular reconstruction via paclitaxel (PTX)-loaded microbubbles (PLM) in a rabbit iliac balloon injury model. PLM was prepared through encapsulating PTX in the shell of lipid microbubbles via film hydration and mechanical vibration technique. Our results showed PLM could effectively deliver PTX when exposed to US irradiation and result in significantly lower viability of vascular smooth muscle cells. Ultrasonographic examinations revealed the US signals from PLM in the iliac artery were greatly increased after intravenous administration of PLM, making it possible to identify the restenosis regions of iliac artery. The in vivo anti-restenosis experiments with PLM and US greatly inhibited neointimal hyperplasia at the injured site, showing an increased lumen area and reduced the ratio of intima area and the media area (I/M ratio). No obvious functional damages to liver and kidney were observed for those animals. Our study provided a promising approach to realize US triggered image-guided PTX delivery for therapeutic applications against iliac restenosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Local administration of NF-kappa B decoy oligonucleotides to prevent restenosis after balloon angioplasty: an experimental study in New Zealand white rabbits.Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2005 May-Jun;28(3):331-7. doi: 10.1007/s00270-003-0239-y. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2005. PMID: 15886949
-
Doxorubicin and paclitaxel loaded microbubbles for ultrasound triggered drug delivery.Int J Pharm. 2011 Jul 29;414(1-2):161-70. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2011.05.030. Epub 2011 May 13. Int J Pharm. 2011. PMID: 21609756 Free PMC article.
-
Poly(vinyl alcohol)-graft-poly(lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles for local delivery of paclitaxel for restenosis treatment.J Control Release. 2007 May 14;119(1):41-51. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2007.01.009. Epub 2007 Jan 26. J Control Release. 2007. PMID: 17346845
-
Enhanced delivery of paclitaxel liposomes using focused ultrasound with microbubbles for treating nude mice bearing intracranial glioblastoma xenografts.Int J Nanomedicine. 2017 Aug 9;12:5613-5629. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S136401. eCollection 2017. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017. PMID: 28848341 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound microbubble-carried PNA targeting to c-myc mRNA inhibits the proliferation of rabbit iliac arterious smooth muscle cells and intimal hyperplasia.Drug Deliv. 2016 Sep;23(7):2482-2487. doi: 10.3109/10717544.2015.1014947. Epub 2015 Mar 2. Drug Deliv. 2016. PMID: 25726989
Cited by
-
Ultrasound-sensitive siRNA-loaded nanobubbles fabrication and antagonism in drug resistance for NSCLC.Drug Deliv. 2022 Dec;29(1):99-110. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2021.2021321. Drug Deliv. 2022. PMID: 34964410 Free PMC article.
-
Power MOSFET Linearizer of a High-Voltage Power Amplifier for High-Frequency Pulse-Echo Instrumentation.Sensors (Basel). 2017 Apr 4;17(4):764. doi: 10.3390/s17040764. Sensors (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28375165 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient ultrasound-mediated drug delivery to orthotopic liver tumors - Direct comparison of doxorubicin-loaded nanobubbles and microbubbles.J Control Release. 2024 Mar;367:135-147. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2024.01.028. Epub 2024 Jan 25. J Control Release. 2024. PMID: 38237687 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasonic technologies in imaging and drug delivery.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Sep;78(17-18):6119-6141. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03904-9. Epub 2021 Jul 23. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 34297166 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficient ultrasound-mediated drug delivery to orthotopic liver tumors - Direct comparison of doxorubicin-loaded nanobubbles and microbubbles.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Sep 5:2023.09.01.555196. doi: 10.1101/2023.09.01.555196. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: J Control Release. 2024 Mar;367:135-147. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2024.01.028. PMID: 37732235 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Poon M., Badimon J. J. & Fuster V. Viewpoint Overcoming restenosis with sirolimus: from alphabet soup to clinical reality. Lancet 359, 619–622 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Yadav J. et al. Protected carotid-artery stenting versus endarterectomy in high-risk patients. New Engl.J. Med. 351, 1493–1501 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Costa M. A. & Simon D. I. Molecular basis of restenosis and drug-eluting stents. Circulation 111, 2257–2273 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Ialenti A. et al. Inhibition of in-stent stenosis by oral administration of bindarit in porcine coronary arteries. Arterioscl. Throm.Vas. 31, 2448–2454 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Katsanos K. et al. Systematic review of infrapopliteal drug-eluting stents: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Cardiovasc. Inter. Rad. 36, 645–658 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

