A potent and selective inhibitor targeting human and murine 12/15-LOX
- PMID: 26899595
- PMCID: PMC4778748
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmc.2016.01.042
A potent and selective inhibitor targeting human and murine 12/15-LOX
Abstract
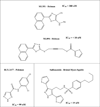
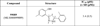
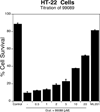
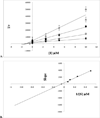
Human reticulocyte 12/15-lipoxygenase (h12/15-LOX) is a lipid-oxidizing enzyme that can directly oxidize lipid membranes in the absence of a phospholipase, leading to a direct attack on organelles, such as the mitochondria. This cytotoxic activity of h12/15-LOX is up-regulated in neurons and endothelial cells after a stroke and thought to contribute to both neuronal cell death and blood-brain barrier leakage. The discovery of inhibitors that selectively target recombinant h12/15-LOX in vitro, as well as possessing activity against the murine ortholog ex vivo, could potentially support a novel therapeutic strategy for the treatment of stroke. Herein, we report a new family of inhibitors discovered in a High Throughput Screen (HTS) that are selective and potent against recombinant h12/15-LOX and cellular mouse 12/15-LOX (m12/15-LOX). MLS000099089 (compound 99089), the parent molecule, exhibits an IC50 potency of 3.4±0.5 μM against h12/15-LOX in vitro and an ex vivo IC50 potency of approximately 10 μM in a mouse neuronal cell line, HT-22. Compound 99089 displays greater than 30-fold selectivity versus h5-LOX and COX-2, 15-fold versus h15-LOX-2 and 10-fold versus h12-LOX, when tested at 20 μM inhibitor concentration. Steady-state inhibition kinetics reveals that the mode of inhibition of 99089 against h12/15-LOX is that of a mixed inhibitor with a Kic of 1.0±0.08 μM and a Kiu of 6.0±3.3 μM. These data indicate that 99089 and related derivatives may serve as a starting point for the development of anti-stroke therapeutics due to their ability to selectively target h12/15-LOX in vitro and m12/15-LOX ex vivo.
Keywords: High-throughput; Human; Inhibitor; Lipoxygenase; Murine; Selective.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Potent and selective inhibitors of human reticulocyte 12/15-lipoxygenase as anti-stroke therapies.J Med Chem. 2014 May 22;57(10):4035-48. doi: 10.1021/jm401915r. Epub 2014 May 13. J Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 24684213 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetic and structural investigations of novel inhibitors of human epithelial 15-lipoxygenase-2.Bioorg Med Chem. 2021 Sep 15;46:116349. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2021.116349. Epub 2021 Aug 5. Bioorg Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34500187 Free PMC article.
-
Biosynthesis of the Maresin Intermediate, 13S,14S-Epoxy-DHA, by Human 15-Lipoxygenase and 12-Lipoxygenase and Its Regulation through Negative Allosteric Modulators.Biochemistry. 2020 May 19;59(19):1832-1844. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.0c00233. Epub 2020 May 7. Biochemistry. 2020. PMID: 32324389 Free PMC article.
-
12/15 Lipoxygenase as a Therapeutic Target in Brain Disorders.Noro Psikiyatr Ars. 2019 Sep 5;56(4):288-291. doi: 10.29399/npa.23646. eCollection 2019 Dec. Noro Psikiyatr Ars. 2019. PMID: 31903039 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of the 12-lipoxygenase pathway in diabetes pathogenesis and complications.Pharmacol Ther. 2019 Mar;195:100-110. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2018.10.010. Epub 2018 Oct 19. Pharmacol Ther. 2019. PMID: 30347209 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Human 15-LOX-1 active site mutations alter inhibitor binding and decrease potency.Bioorg Med Chem. 2016 Nov 1;24(21):5380-5387. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2016.08.063. Epub 2016 Aug 31. Bioorg Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27647374 Free PMC article.
-
The Chemical Biology of Ferroptosis in the Central Nervous System.Cell Chem Biol. 2020 May 21;27(5):479-498. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2020.03.007. Epub 2020 Apr 2. Cell Chem Biol. 2020. PMID: 32243811 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Redox mechanism of glycerophospholipids and relevant targeted therapy in ferroptosis.Cell Death Discov. 2025 Aug 1;11(1):358. doi: 10.1038/s41420-025-02654-y. Cell Death Discov. 2025. PMID: 40744916 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contributions of 12/15-Lipoxygenase to Bleeding in the Brain Following Ischemic Stroke.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1161:125-131. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-21735-8_12. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 31562627 Free PMC article.
-
Recent development of lipoxygenase inhibitors as anti-inflammatory agents.Medchemcomm. 2017 Nov 29;9(2):212-225. doi: 10.1039/c7md00390k. eCollection 2018 Feb 1. Medchemcomm. 2017. PMID: 30108915 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Research Materials

