Oral L-citrulline supplementation enhances cycling time trial performance in healthy trained men: Double-blind randomized placebo-controlled 2-way crossover study
- PMID: 26900386
- PMCID: PMC4759860
- DOI: 10.1186/s12970-016-0117-z
Oral L-citrulline supplementation enhances cycling time trial performance in healthy trained men: Double-blind randomized placebo-controlled 2-way crossover study
Abstract
Background: Many human studies report that nitric oxide (NO) improves sport performance. This is because NO is a potential modulator of blood flow, muscle energy metabolism, and mitochondrial respiration during exercise. L-Citrulline is an amino acid present in the body and is a potent endogenous precursor of L-arginine, which is a substrate for NO synthase. Here, we investigated the effect of oral L-citrulline supplementation on cycling time trial performance in humans.
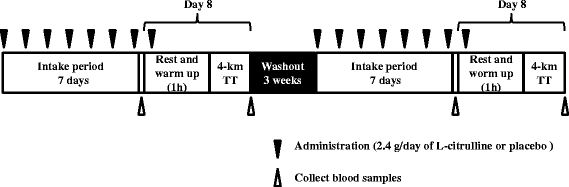
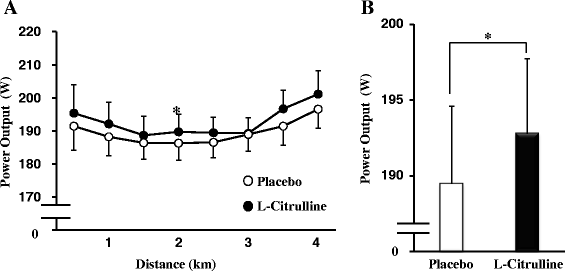
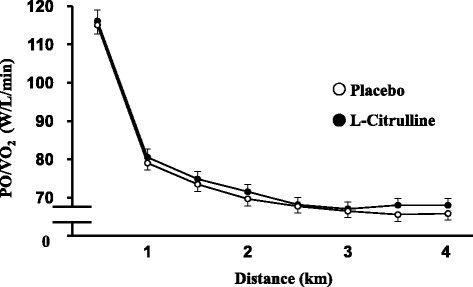
Methods: A double-blind randomized placebo-controlled 2-way crossover study was employed. Twenty-two trained males consumed 2.4 g/day of L-citrulline or placebo orally for 7 days. On Day 8 they took 2.4 g of L-citrulline or placebo 1 h before a 4-km cycling time trial. Time taken to complete the 4 km cycle, along with power output/VO2 ratio (PO/VO2), plasma nitrite and nitrate (NOx) and amino acid levels, and visual analog scale (VAS) scores, was evaluated.
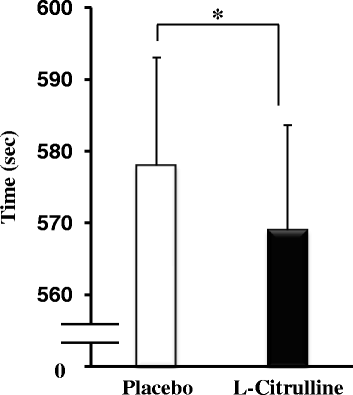
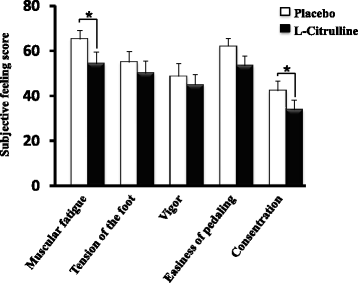
Results: L-Citrulline supplementation significantly increased plasma L-arginine levels and reduced completion time by 1.5 % (p < 0.05) compared with placebo. Moreover, L-citrulline significantly improved subjective feelings of muscle fatigue and concentration immediately after exercise.
Conclusions: Oral L-citrulline supplementation reduced the time take to complete a cycle ergometer exercise trial.
Trial registration: Current Controlled Trials UMIN000014278.
Keywords: Ergogenic; Human; L-Citrulline; Nitric oxide (NO); Sport performance.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
