Long-term Metformin Use and Vitamin B12 Deficiency in the Diabetes Prevention Program Outcomes Study
- PMID: 26900641
- PMCID: PMC4880159
- DOI: 10.1210/jc.2015-3754
Long-term Metformin Use and Vitamin B12 Deficiency in the Diabetes Prevention Program Outcomes Study
Abstract
Context: Vitamin B12 deficiency may occur with metformin treatment, but few studies have assessed risk with long-term use.
Objective: To assess the risk of B12 deficiency with metformin use in the Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP)/DPP Outcomes Study (DPPOS).
Design: Secondary analysis from the DPP/DPPOS. Participants were assigned to the placebo group (PLA) (n = 1082) or the metformin group (MET) (n = 1073) for 3.2 years; subjects in the metformin group received open-label metformin for an additional 9 years.
Setting: Twenty-seven study centers in the United States.
Patients: DPP eligibility criteria were: elevated fasting glucose, impaired glucose tolerance, and overweight/obesity. The analytic population comprised participants with available stored samples. B12 levels were assessed at 5 years (n = 857, n = 858) and 13 years (n = 756, n = 764) in PLA and MET, respectively.
Intervention: Metformin 850 mg twice daily vs placebo (DPP), and open-label metformin in the metformin group (DPPOS).
Main outcome measures: B12 deficiency, anemia, and peripheral neuropathy.
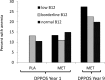
Results: Low B12 (≤ 203 pg/mL) occurred more often in MET than PLA at 5 years (4.3 vs 2.3%; P = .02) but not at 13 years (7.4 vs 5.4%; P = .12). Combined low and borderline-low B12 (≤ 298 pg/mL) was more common in MET at 5 years (19.1 vs 9.5%; P < .01) and 13 years (20.3 vs 15.6%; P = .02). Years of metformin use were associated with increased risk of B12 deficiency (odds ratio, B12 deficiency/year metformin use, 1.13; 95% confidence interval, 1.06–1.20). Anemia prevalence was higher in MET, but did not differ by B12 status. Neuropathy prevalence was higher in MET with low B12 levels.
Conclusions: Long-term use of metformin in DPPOS was associated with biochemical B12 deficiency and anemia. Routine testing of vitamin B12 levels in metformin-treated patients should be considered.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00038727.
Figures
Comment in
-
Diabetes: Metformin linked to vitamin B12 deficiency.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2016 Jun;12(6):312. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2016.39. Epub 2016 Mar 11. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2016. PMID: 26965381 No abstract available.
References
-
- Berchtold P, Bolli P, Arbenz U, Keiser G. Disturbance of intestinal absorption following metformin therapy (observations on the mode of action of biguanides) [in German]. Diabetologia. 1969;5:405–412. - PubMed
-
- Beulens JW, Hart HE, Kuijs R, Kooijman-Buiting AM, Rutten GE. Influence of duration and dose of metformin on cobalamin deficiency in type 2 diabetes patients using metformin. Acta Diabetol. 2015;52:47–53. - PubMed
-
- de Groot-Kamphuis DM, van Dijk PR, Groenier KH, Houweling ST, Bilo HJ, Kleefstra N. Vitamin B12 deficiency and the lack of its consequences in type 2 diabetes patients using metformin. Neth J Med. 2013;71:386–390. - PubMed
-
- Haeusler S, Parry-Strong A, Krebs JD. The prevalence of low vitamin B12 status in people with type 2 diabetes receiving metformin therapy in New Zealand–a clinical audit. N Z Med J. 2014;127:8–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- U01 DK048412/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048375/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048434/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048413/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048468/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048387/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048404/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048407/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048437/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048406/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001409/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK078907/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048397/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048381/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048514/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048485/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048411/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020541/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048443/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048380/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048400/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048489/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048349/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048377/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK017047/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous