Specific Neuropilins Expression in Alveolar Macrophages among Tissue-Specific Macrophages
- PMID: 26900851
- PMCID: PMC4764655
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147358
Specific Neuropilins Expression in Alveolar Macrophages among Tissue-Specific Macrophages
Abstract
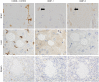
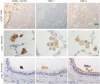
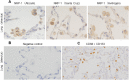
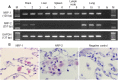
In the immune system, neuropilins (NRPs), including NRP-1 and NRP-2, are expressed in thymocytes, dendritic cells, regulatory T cells and macrophages. Their functions on immune cells around the neoplastic cells vary into pro-angiogenesis, tumor progression and anti-angiogenesis according to their ligands. Even though NRPs expression on malignant tumors and immune system has studied, a PubMed-based literature query did not yield any articles describing NRPs expression on tissue-specific macrophages. The aims of this study were (i) to detect NRPs expression on tissue-specific macrophages in the brain, liver, spleen, lymph node and lung; (ii) to observe NRPs expression in classes of macrophages, including alveolar macrophages (AMs), bronchial macrophages (BMs), interstitial macrophages (IMs), intravascular macrophages (IVMs) and macrophage subsets (M1, M2 and Mox) in lung; and (iii) to detect the co-expression of NRPs and dendritic cell-specific ICAM-3-grabbing nonintegrin (DC-SIGN) in AMs. Both NRPs were specifically detected in AMs among tissue-specific macrophages by immunohistochemistry (IHC). NRPs mRNA expression levels were characterized in normal lung by reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and in situ-polymerase chain reaction (in situ-PCR). The expression of both NRPs was detected in AMs, BMs and IVMs by IHC. The frequency of NRPs+ AMs in lung tissue adjacent to the cancer margin was significantly higher than the frequencies in inflamed and normal lung tissue. Double and triple IHC demonstrated that NRPs are expressed on all macrophage subsets in lung. Double IHC showed co-expression of DC-SIGN and NRPs in AMs. This study demonstrated for the first time the specific expression of both NRPs in AMs among tissue-specific macrophages and their expression on M1, M2 and Mox macrophages. Furthermore, the possible origin of AMs from blood monocytes could be suggested from a co-expression of NRPs and DC-SIGN.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Fujisawa H. Discovery of semaphorine receptors, neuropilin and plexin, and their functions in neural development. J Neurobiol. 2004;59:24–33. - PubMed
-
- West DC, Rees CG, Duchesne L, Patey SJ, Terry CJ, Turnbull JE, et al. Interactions of multiple heparin binding growth factors with neuropilin-1 and potentiation of the activity of fibroblast growth factor-2. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:13457–13464. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

