Diurnal Corticosterone Presence and Phase Modulate Clock Gene Expression in the Male Rat Prefrontal Cortex
- PMID: 26901093
- PMCID: PMC4816727
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2015-1884
Diurnal Corticosterone Presence and Phase Modulate Clock Gene Expression in the Male Rat Prefrontal Cortex
Abstract
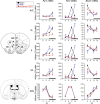
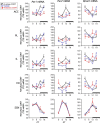
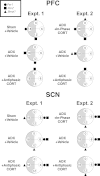
Mood disorders are associated with dysregulation of prefrontal cortex (PFC) function, circadian rhythms, and diurnal glucocorticoid (corticosterone [CORT]) circulation. Entrainment of clock gene expression in some peripheral tissues depends on CORT. In this study, we characterized over the course of the day the mRNA expression pattern of the core clock genes Per1, Per2, and Bmal1 in the male rat PFC and suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) under different diurnal CORT conditions. In experiment 1, rats were left adrenal-intact (sham) or were adrenalectomized (ADX) followed by 10 daily antiphasic (opposite time of day of the endogenous CORT peak) ip injections of either vehicle or 2.5 mg/kg CORT. In experiment 2, all rats received ADX surgery followed by 13 daily injections of vehicle or CORT either antiphasic or in-phase with the endogenous CORT peak. In sham rats clock gene mRNA levels displayed a diurnal pattern of expression in the PFC and the SCN, but the phase differed between the 2 structures. ADX substantially altered clock gene expression patterns in the PFC. This alteration was normalized by in-phase CORT treatment, whereas antiphasic CORT treatment appears to have eliminated a diurnal pattern (Per1 and Bmal1) or dampened/inverted its phase (Per2). There was very little effect of CORT condition on clock gene expression in the SCN. These experiments suggest that an important component of glucocorticoid circadian physiology entails CORT regulation of the molecular clock in the PFC. Consequently, they also point to a possible mechanism that contributes to PFC disrupted function in disorders associated with abnormal CORT circulation.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Coordination between Prefrontal Cortex Clock Gene Expression and Corticosterone Contributes to Enhanced Conditioned Fear Extinction Recall.eNeuro. 2018 Dec 21;5(6):ENEURO.0455-18.2018. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0455-18.2018. eCollection 2018 Nov-Dec. eNeuro. 2018. PMID: 30627637 Free PMC article.
-
Adrenal-dependent and -independent stress-induced Per1 mRNA in hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus and prefrontal cortex of male and female rats.Stress. 2018 Jan;21(1):69-83. doi: 10.1080/10253890.2017.1404571. Epub 2017 Nov 22. Stress. 2018. PMID: 29165002
-
Variations in Phase and Amplitude of Rhythmic Clock Gene Expression across Prefrontal Cortex, Hippocampus, Amygdala, and Hypothalamic Paraventricular and Suprachiasmatic Nuclei of Male and Female Rats.J Biol Rhythms. 2015 Oct;30(5):417-36. doi: 10.1177/0748730415598608. Epub 2015 Aug 13. J Biol Rhythms. 2015. PMID: 26271538 Free PMC article.
-
Rhythmic Release of Corticosterone Induces Circadian Clock Gene Expression in the Cerebellum.Neuroendocrinology. 2020;110(7-8):604-615. doi: 10.1159/000503720. Epub 2019 Sep 27. Neuroendocrinology. 2020. PMID: 31557761
-
Altered rhythm of adrenal clock genes, StAR and serum corticosterone in VIP receptor 2-deficient mice.J Mol Neurosci. 2012 Nov;48(3):584-96. doi: 10.1007/s12031-012-9804-7. Epub 2012 May 24. J Mol Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22622901
Cited by
-
Circadian Clock Genes Are Regulated by Rhythmic Corticosterone at Physiological Levels in the Rat Hippocampus.Neuroendocrinology. 2023;113(10):1076-1090. doi: 10.1159/000533151. Epub 2023 Jul 29. Neuroendocrinology. 2023. PMID: 37517388 Free PMC article.
-
Hsp90 Heterocomplexes Regulate Steroid Hormone Receptors: From Stress Response to Psychiatric Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Dec 25;20(1):79. doi: 10.3390/ijms20010079. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30585227 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Intact Krüppel-like factor 9 Gene Is Required for Acute Liver Period 1 mRNA Response to Restraint Stress.Endocrinology. 2021 Sep 1;162(9):bqab083. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqab083. Endocrinology. 2021. PMID: 33904929 Free PMC article.
-
Coordination between Prefrontal Cortex Clock Gene Expression and Corticosterone Contributes to Enhanced Conditioned Fear Extinction Recall.eNeuro. 2018 Dec 21;5(6):ENEURO.0455-18.2018. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0455-18.2018. eCollection 2018 Nov-Dec. eNeuro. 2018. PMID: 30627637 Free PMC article.
-
The Paralogous Krüppel-like Factors 9 and 13 Regulate the Mammalian Cellular Circadian Clock Output Gene Dbp.J Biol Rhythms. 2020 Jun;35(3):257-274. doi: 10.1177/0748730420913205. Epub 2020 Apr 3. J Biol Rhythms. 2020. PMID: 32241200 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hastings MH, Reddy AB, Maywood ES. A clockwork web: circadian timing in brain and periphery, in health and disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2003;4(8):649–661. - PubMed
-
- Bunney JN, Potkin SG. Circadian abnormalities, molecular clock genes and chronobiological treatments in depression. Br Med Bull. 2008;86(1):23–32. - PubMed
-
- Yehuda R. Biology of posttraumatic stress disorder. J Clin Psychiatry. 2001;62(suppl 17):41–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

